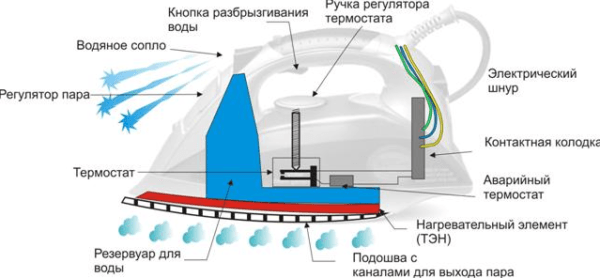
Iron device: its electrical circuit and principle of operation
The principle of operation and internal structure of the iron, at first sight, do not raise special questions: electric current leads to heating of the nichrome spiral, which, in turn, transfers heat to a massive metal plate - the sole. But how is the heating temperature regulated, steam supply or water spray? Modern models of irons can be equipped with various systems to prevent the formation of scale, electronic components and regulators, the presence of which significantly complicates the design.
It is not easy to understand the device of a modern iron on your own, however, having such information can help troubleshoot minor issues. Due to the high complexity of the iron design, for overhaul (replacement of spirals or electronic components, purification water pumps, restoration of an electric wire) recommend contacting specialized workshops, as the operation of the device after unauthorized interference is not guaranteed.
What parts does the iron consist of??
This is a familiar household appliance, like an iron, is quite complex, from a technical point of view, device. The scheme of the iron includes several dozen elements, the main among which are the heating element, thermostat, overheat protection system, as well as various regulators, indicators and other electronic components, without which it is impossible to imagine the normal operation of a modern iron.
How a modern iron is arranged, many models of which can be seen today on store shelves? First of all, the following components should be distinguished in its structure:
- electric wire;
- steam supply system;
- water chamber and steam generators;
- sole;
- thermostat.
Considering each of the elements separately, special attention should be paid to the internal structure and principle of operation of parts, as such information makes it possible to determine the cause of breakdowns and ways to eliminate them.
Electric wire
Although at first glance the wire for the iron is no different from a similar element of other appliances, in its appearance and internal structure some features are traced: first of all, the wire has a fabric braid, which prevents the grinding of the polymer shell during ironing.
It is difficult to imagine any other device, which is subjected to the same heavy load, like an iron, after all at its use it is necessary to twist a cable in different directions several times, stretch it, bend at unthinkable angles and even carelessly fold into a knot.
An ordinary cord would not be able to withstand such manipulations for long, while the iron wire does its job perfectly for years or even decades.
The secret lies in the fabric braid: it reduces the coefficient of friction between different sections of the cable several times, and also increases its rigidity. As an additional element, which adds maximum system reliability, a plastic limiter is used, which is located at the base of the iron and is designed for that, to prevent possible wire bends.
The inner part of the iron wire is presented ??three veins, one of which is used as grounding. This safety measure reduces the risk of electric shock in the event of a short circuit and prolongs the life of the device..
Steam supply system
Most modern models of irons are equipped with two buttons, which are located in front of the device: one of them is responsible for supplying steam, and the other gives the opportunity, if necessary, to moisten the fabric by spraying water through a special hole, located on the spout of the iron. The conversion of water into steam takes place in a separate chamber, which is equipped with powerful heating elements. After pressing the button, the pressurized liquid enters the chamber, where it instantly heats up, and is distributed through the perforation on the soleplate of the iron.
The use of untreated tap water often leads to excessive formation of carbonate deposits on the surface of the heaters, which naturally entails a decrease in heating efficiency, and failure of heating elements. The appearance of traces of rust, dirt or scale debris on fabrics during ironing is an alarm signal, which indicates, it's time to pay extra attention to cleaning the iron.
Sole and heater system
From the sole, as the main component of the iron, largely depends not only on the quality of ironing, but also the overall level of comfort when using the device. Manufacturers of modern irons will equip them with Teflon soles, ceramic or even sapphire coating - this technical solution reduces the coefficient of friction between the sole and fabric, thus facilitating the ironing process. Inexpensive models of irons are equipped with an aluminum sole, the main disadvantage of which is the excessive pliability of the metal, which often leads to noticeable scratches.
Inside the sole is a heating element - nichrome spiral, supplemented with ceramic rings, which evenly distribute heat and help to keep it for a long time. The heating temperature is set by a separate thermostat, the main function of which is the timely disconnection of electricity supply in accordance with the specified mode.
Temperature regulator and heating shut-off system
The use of an iron on different types of fabrics involves careful selection of the appropriate temperature.
In most cases, ironing requirements are specified by clothing manufacturers on a separate label, which is sewn into the folds of the product.
Heating control is carried out by installing the rotary wheel of the iron in the desired position, corresponding to the permissible ironing parameters. When the temperature reaches its maximum value, the contact is opened, as a result, the supply voltage is stopped.
How the regulator is disconnected? Electrical circuits of irons assume the presence of a special element - a bimetallic plate, which consists of two parts, made of metals with different coefficients of thermal expansion. When heated, the metal is deformed, and differences in the properties of the components of the plate lead to slight deformation, as a result, the plate is moved up and stops coming into contact with the electrical circuit. A similar principle of operation is used not only in irons, but also in teapots, relays for switching off boilers and other heating elements.
Typical iron malfunctions and ways to solve them
Iron failures are mainly due to improper operation, sharp voltage drops or insufficient tightness of the water compartment, moisture from which leaks to the electronic components of the device. Determine the cause of the fault, given the significant complexity of the design of modern irons, it is not easy, however, there are a number of typical features, which reduce the range of searches:
- When the iron is connected to the mains, the light does not light up and the sole does not heat up. First of all it is necessary to check up serviceability of the socket, because it is often the cause of failure. If the network is working, then the next source of the problem may be a violation of the integrity of the network cable. in addition, the break is often found directly in the soleplate of the iron, where a small fuse is located, burns out when overheated.
- The indicator is lit., but the heating does not work. In this case, look for the cause of the fault in the heating element or the fuse described above, since energy supply to the sole depends on these elements.
- During the supply of steam from the holes in the sole begins to seep rusty water with fragments of scale. A similar problem is observed when some moisture gets directly on the electronic components of the iron: during contact, when the device is switched on with moisture, an electrochemical reaction occurs, which leads to the slow destruction of the metal. The process is intensified with the use of water, which contains a large amount of salts, organic and inorganic impurities.
How to extend the life of the iron?
In order for the iron to last you as long as possible and not cause problems with its work, Here are some simple tips:
- Avoid careless handling of the iron: electronic components of the device do not tolerate sharp shocks, temperature drops or fluctuations. If your iron is equipped with a ceramic sole, then his vulnerability, due to the fragility of the material, significantly increases.
- It is recommended to use distilled water or a special flavored liquid to fill the iron, which can be found in the departments of household chemicals. It is absolutely unacceptable to use even purified water or to fill the iron directly from the tap, since such treatment leads to the rapid accumulation of carbonate and iron deposits.
- If you store the iron on the balcony or elsewhere, the temperature in which differs significantly from room temperature, then after moving the iron in a warm room, it is recommended to allow it a little "acclimatize", due to which all the condensate, which settles on the contacts, will have time to evaporate.
- Any pollution, appearing on the metal sole, should be removed immediately by special means. Ironing of plastic elements is also not allowed, lightning, decorative drawings, sequins and prints, because they melt quite easily and can greatly contaminate the sole.
The main principle of irons is to evenly heat the metal sole and the distribution of water vapor in the fabric. Following simple precautions, you will not only be able to significantly extend the life of the equipment, but also to avoid most common breakdowns.