Calculation of current strength and selection of power cable for mains voltage 220 and 380 V
To ensure safety in the operation of household appliances, it is necessary to correctly calculate the cross section of the power cable and wiring. Because an incorrectly selected cable core cross section creates a risk of ignition wiring due to a short circuit. This threatens to cause a fire in the building. This also applies to the choice of cable for connecting electric motors.
current calculation
The amount of current is calculated by power and required at the design stage (planning) housing - apartments, houses.
- The choice of power cable depends on the value of this value (wire), which can be used to connect electricity appliances to the grid.
- Knowing the mains voltage and the full load of electrical appliances, you can calculate the current strength by the formula, which will need to be passed through the conductor (wire, cable). According to its size, choose the cross-sectional area of the veins.
If known consumers in the apartment or house, it is necessary to perform simple calculations, to properly mount the power supply circuit.
Similar calculations are performed for production purposes: determining the required cross-sectional area of the cable cores when connecting industrial equipment (various industrial electric motors and mechanisms).
Single-phase mains voltage 220 V
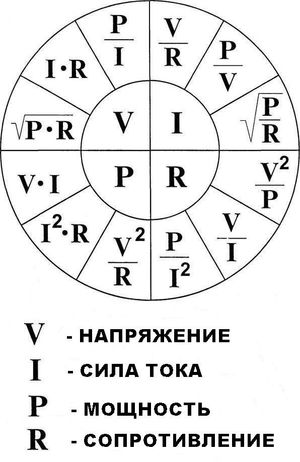
Current strength I (in amperes, A) calculated by the formula:
I = P / U,
where P is the electric full load (must be specified in the technical data sheet of the device), W (watts);
U - mains voltage, V (volt).
The table below shows the load values of typical household appliances and the current consumed by them (for voltage 220 V).
| Electrical appliance | Power consumption, W | Amperage, A |
| Washing machine | 2000 — 2500 | 9,0 — 11,4 |
| jacuzzi | 2000 — 2500 | 9,0 — 11,4 |
| electric floor heating | 800 — 1400 | 3,6 — 6,4 |
| Stationary electric stove | 4500 — 8500 | 20,5 — 38,6 |
| Microwave oven | 900 — 1300 | 4,1 — 5,9 |
| Dishwashers | 2000 — 2500 | 9,0 — 11,4 |
| Freezers, refrigerators | 140 — 300 | 0,6 — 1,4 |
| Electric meat grinder | 1100 — 1200 | 5,0 — 5,5 |
| electric kettle | 1850 — 2000 | 8,4 — 9,0 |
| electric coffee maker | 6з0 - 1200 | 3,0 — 5,5 |
| Squeezer | 240 — 360 | 1,1 — 1,6 |
| toaster | 640 — 1100 | 2,9 — 5,0 |
| mixer | 250 — 400 | 1,1 — 1,8 |
| hair dryer | 400 — 1600 | 1,8 — 7,3 |
| iron | 900 — 1700 | 4,1 — 7,7 |
| Vacuum cleaner | 680 — 1400 | 3,1 — 6,4 |
| fan | 250 — 400 | 1,0 — 1,8 |
| TV | 125 — 180 | 0,6 — 0,8 |
| radio equipment | 70 — 100 | 0,3 — 0,5 |
| lighting devices | 20 — 100 | 0,1 — 0,4 |
The figure shows ??the scheme of the device of power supply of the apartment at single-phase connection to a network with voltage 220 V.
As can be seen from the figure, various consumers of electricity are connected through appropriate machines to electricity meters and then to the general machine, which must be designed to load the devices, what the apartment will be equipped with. Wire, supplying power must also meet the load of energy consumers.
Below is a table for concealed wiring with a single-phase connection diagram of the apartment for the selection of wires at voltage 220 V
| Intersection of wire wires, mm2 | The diameter of the conductor core, mm | copper cores | aluminum cores | ||
| Current, A | Power, W | Current, A | Power, kw | ||
| 0,50 | 0,80 | 6 | 1300 | ||
| 0,75 | 0,98 | 10 | 2200 | ||
| 1,00 | 1,13 | 14 | 3100 | ||
| 1,50 | 1,38 | 15 | 3300 | 10 | 2200 |
| 2,00 | 1,60 | 19 | 4200 | 14 | 3100 |
| 2,50 | 1,78 | 21 | 4600 | 16 | 3500 |
| 4,00 | 2,26 | 27 | 5900 | 21 | 4600 |
| 6,00 | 2,76 | 34 | 7500 | 26 | 5700 |
| 10,00 | 3,57 | 50 | 11000 | 38 | 8400 |
| 16,00 | 4,51 | 80 | 17600 | 55 | 12100 |
| 25,00 | 5,64 | 100 | 22000 | 65 | 14300 |
As can be seen from the table, the cross section of the veins depends not only on the load but also on the material, of which the wire is made.
Three-phase mains voltage 380 V
In three-phase power supply current I (in amperes, A) calculated by the formula:
I = P / 1,73 U,
where P -power consumption, W;
U - mains voltage, V,
since the voltage in a three-phase power supply circuit 380 V, the formula will take the form:
I = P / 657, 4.
In the case of supply to the house three-phase power supply voltage 380 The wiring diagram will look like this.
The section lived in the power cable at different loads in a three-phase voltage circuit 380 In for hidden wiring is presented ??in the table.
| Intersection of wire wires, mm2 | The diameter of the conductor core, mm | copper cores | aluminum cores | ||
| Current, A | Power, W | Current, A | Power, kw | ||
| 0,50 | 0,80 | 6 | 2250 | ||
| 0,75 | 0,98 | 10 | 3800 | ||
| 1,00 | 1,13 | 14 | 5300 | ||
| 1,50 | 1,38 | 15 | 5700 | 10 | 3800 |
| 2,00 | 1,60 | 19 | 7200 | 14 | 5300 |
| 2,50 | 1,78 | 21 | 7900 | 16 | 6000 |
| 4,00 | 2,26 | 27 | 10000 | 21 | 7900 |
| 6,00 | 2,76 | 34 | 12000 | 26 | 9800 |
| 10,00 | 3,57 | 50 | 19000 | 38 | 14000 |
| 16,00 | 4,51 | 80 | 30000 | 55 | 20000 |
| 25,00 | 5,64 | 100 | 38000 | 65 | 24000 |
To calculate the current in the load supply circuits, characterized by high reactive full power, which is typical of the use of electricity in industry:
- electric motors;
- chokes of lighting devices;
- welding transformers ,;
- induction furnaces.
This phenomenon must be taken into account in the calculations. In powerful devices and equipment the share of reactive loading is higher and therefore for such devices in calculations the power factor is accepted equal 0,8.
In practice, it is considered, that when calculating electrical loads for domestic purposes, the power reserve is taken 5%. In the case of calculation of electrical networks for industrial production, the power reserve is accepted 20%.



