
Nitriding of steel: purpose and features of technology
Nitriding, in the process of which the surface layer of the steel product is saturated with nitrogen, began to be used on an industrial scale relatively recently. This method of processing, proposed for use by Academician NP. Chizhevsky, allows to improve many characteristics of products, made of steel alloys.

Ion-vacuum nitriding shop
The essence of technology
Nitriding of steel, if you compare it with such a popular method of metal processing, as cementation, has a number of significant advantages. That is why this technology has been used as the main way to improve the quality characteristics of steel.
When nitriding steel product is not exposed to significant thermal effects, while the hardness of its surface layer increases significantly. Importantly, that the sizes of the nitrided details do not change. This allows the use of this method of processing for steel products, which have already passed hardening with high tempering and polished to the required geometric parameters. After nitriding, or nitriding, as this process is often called, steel can be immediately put to polishing or other finishing methods.
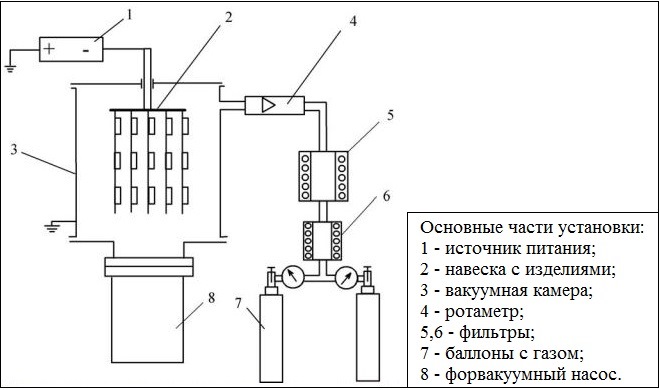
Scheme of nitriding installation in the glow discharge
Nitriding of steel is, that the metal is heated in the medium, characterized by a high content of ammonia. As a result of such processing with a surface layer of metal, saturable nitrogen, the following changes occur.
- Due to that, that the hardness of the surface layer of steel increases, improves the wear resistance of the part.
- The fatigue strength of the product increases.
- The surface of the product becomes resistant to corrosion. This stability is maintained by contact of steel with water, humid air and steam-air environment.
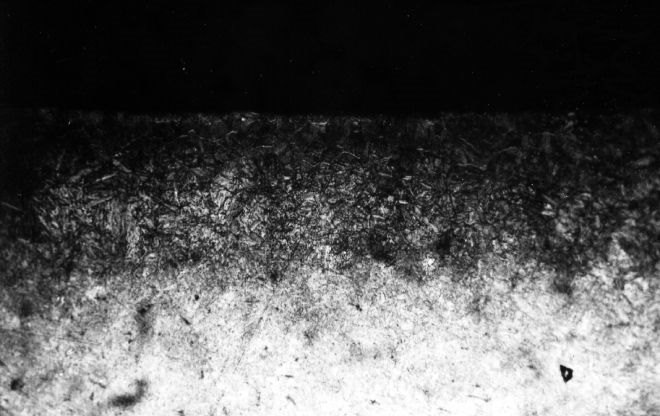

Microstructure of high-quality nitrided steel layer grade 38Х2МЮА
Execution of nitriding allows to receive more stable indicators of hardness of steel, than in the implementation of cementation. So, surface layer of the product, which was subjected to nitriding, retains its hardness even when heated to a temperature of 550-600 °, while after cementation the hardness of the surface layer may begin to decrease when the product is heated above 225 °. The strength characteristics of the steel surface layer after nitriding are 1.5–2 times higher, than after hardening or cementation.
How the nitriding process takes place
Metal parts are placed in a hermetically sealed muffle, which is then installed in the nitriding furnace. In the furnace, the muffle with the part is heated to the temperature, which is usually in the range of 500-600 °, and then stand for some time at this temperature.

Vacuum furnace for heat treatment with gas nitriding system
To form a working environment inside the muffle, required for nitriding, ammonia is supplied to it under pressure. Warming up, ammonia begins to decompose into constituent elements, this process is described by the following chemical formula:
2NH3 > 6H + 2N.
Atomic nitrogen, released in the process of such a reaction, reason diffuse into metal, from which the workpiece is made, which leads to the formation of nitrides on its surface, characterized by high hardness. To consolidate the result and prevent the surface of the part from oxidizing, muffle together with the product and ammonia, which continues to remain in it, slowly cool together with the nitriding furnace.
Nitride ball, which is formed on the metal surface during nitriding, may have a thickness in the range of 0.3-0.6 mm. That's enough for that, to give the product the necessary strength characteristics. Steel treated with this technology can not be subjected to any additional processing methods.
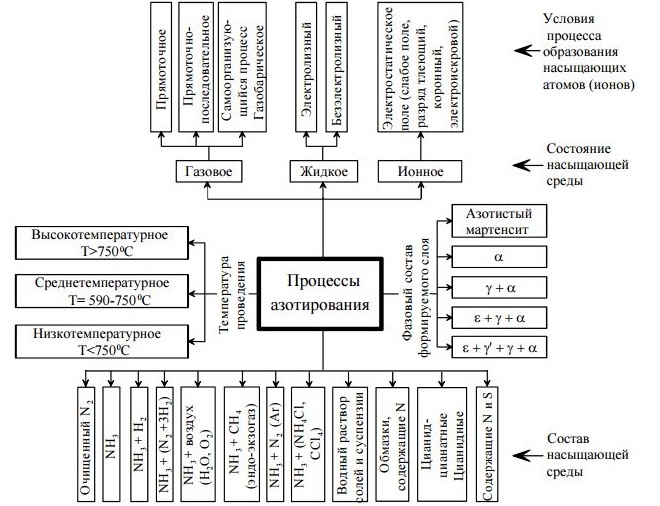
Classification of nitriding processes
Processes, flowing in the surface layer of the steel product during its nitriding, quite complex, but already well studied by specialists in the metallurgical industry. As a result of such processes in the structure of the processed metal the following phases are formed:
- solid solution of Fe3N, characterized by a nitrogen content within 8-11,2%;
- solid solution of Fe4N, nitrogen which contains 5.7-6.1%;
- nitrogen solution, formed in ?-gland.
Additionally ?-phase in the metal structure is formed then, when the nitriding temperature begins to exceed 591 °. At that moment, when the degree of saturation of this phase with nitrogen reaches its maximum, a new phase is formed in the metal structure. Eutectoid decay in the metal structure occurs then, when the degree of its nitrogen saturation reaches the level 2,35%.

The valves of high-tech internal combustion engines must undergo a nitriding process
Factors, affecting nitriding
The main factors, which affect nitriding, is:
- temperature, in which such a technological operation is performed;
- gas pressure, fed into the muffle;
- the duration of exposure of the part in the furnace.
The efficiency of this process is also affected by the degree of dissociation of ammonia, which, usually, is in the interval 15-45%. As the nitriding temperature increases, the hardness of the formed layer decreases, but the process of diffusion of nitrogen into the metal structure is accelerated. The decrease in the hardness of the surface layer of the metal during its nitriding occurs by coagulation of nitrides of alloying elements, which are part of it.
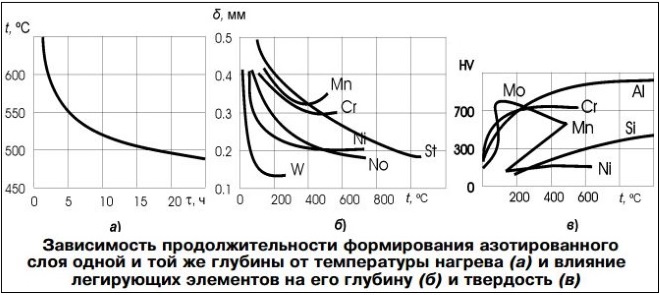
Influence of temperature and alloying elements on the formation of the nitrided layer
To speed up the nitriding process and increase its efficiency, a two-stage scheme of its implementation is used. The first stage of nitriding using such a scheme is performed at temperature, not exceeding 525 °. This allows to give the surface layer of the steel product high hardness. To perform the second stage of the procedure, the part is heated to a temperature of 600-620 °, the depth of the nitrided layer reaches the required values, and the process itself is accelerated almost twice. Hardness of the surface layer of the steel product, processed by such technology, not below, than a similar parameter of products, processed by direct methods.
Types of nitrided steels
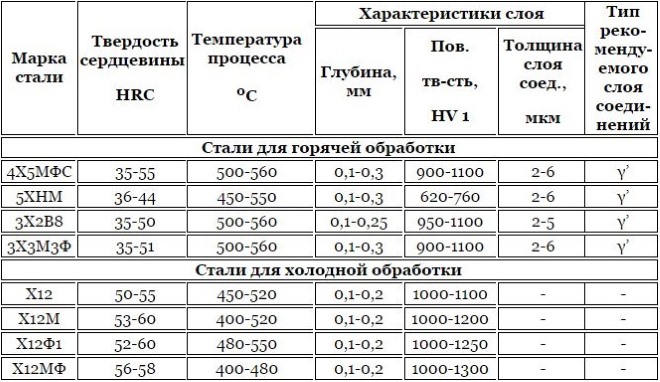
Nitriding treatments can be treated as carbon, and alloy steels, characterized by a carbon content in the range of 0.3-0.5%. The maximum effect when using such technological operation can be reached in that case, if it is exposed to steel, chemical composition of which includes alloying elements, forming solid and heat-resistant nitrides. To such elements, in particular, belong to molybdenum, aluminum, chrome and other metals, having similar characteristics. Become, containing molybdenum, not prone to such a negative phenomenon, as holiday fragility, which occurs during slow cooling of the steel product. After nitriding steels of different grades acquire such hardness:
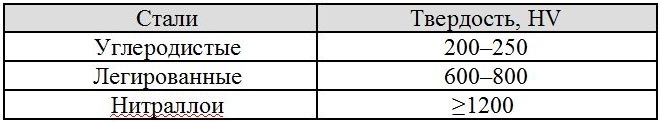
Hardness of steels after nitriding
Alloying elements, contained in the chemical composition of steel, increase the hardness of the nitrided layer, but at the same time reduce its thickness. The thickness of the nitrided layer is most actively influenced by the following chemical elements, like tungsten, molybdenum, chrome and nickel.
Depending on the scope of the product, subjected to the nitriding procedure, and also from conditions of its operation for implementation of such technological operation it is recommended to use certain grades of steel. So, in accordance with the technological task, which needs to be addressed, Experts advise to use for nitriding products from the following grades of steel.
38Х2МЮА
This is steel, which after nitriding has a high hardness of the outer surface. Aluminum, contained in the chemical composition of such steel, reduces the deformation resistance of the product, but at the same time helps to increase the hardness and wear resistance of its outer surface. The exclusion of aluminum from the chemical composition of steel allows you to create products from it of complex configuration.
40X, 40HFA
These alloy steels are used to make parts, used in the field of machine tools.
30Х3М, 38HGM, 38HNMFA, 38HN3MA
These steels are used for the production of products, subjected to frequent cyclic bending loads during operation.
30Х3МФ1
Products are made of this steel alloy, the accuracy of geometric parameters which are subject to high requirements. To give higher hardness to parts made of this steel (these are mainly parts of fuel equipment) silicon can be added to its chemical composition.
Characteristics of some steels after nitriding
Technological scheme of nitriding
To perform traditional gas nitriding, innovative plasma nitriding or ionic nitriding, the workpiece is subjected to a number of technological operations.
Preparatory heat treatment
Such processing consists in hardening of a product and its high holiday. Hardening as part of this procedure is carried out at a temperature of about 940 °, while cooling the processed product is performed in oil or water. The next vacation after hardening, takes place at a temperature of 600-700 °, allows to endow the processed metal with hardness, at which it can be easily cut.
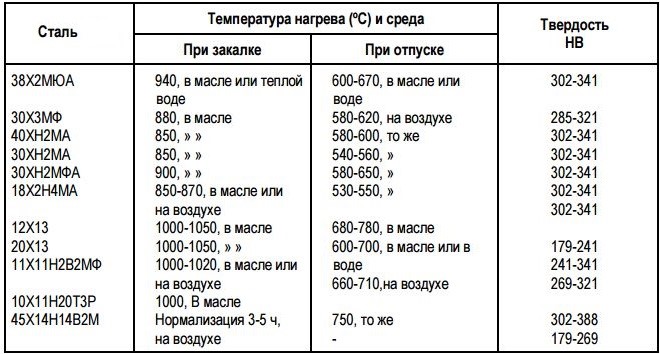
Heat treatment modes before nitriding
Tooling
This operation ends with its grinding, which allows to bring the geometric parameters of the part to the required values.
Protection of product areas, which do not require nitriding
Such protection is carried out by applying a thin layer (not more 0,015 mm) tin or liquid glass. Electrolysis technology is used for this purpose. Film from these materials, formed on the surface of the product, does not allow nitrogen to penetrate into its internal structure.
Execution of nitriding itself
The prepared product is subjected to processing in a gaseous medium.
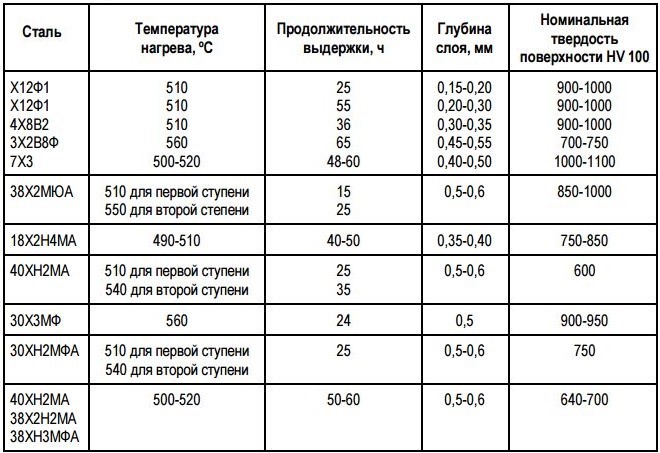
Recommended modes of nitriding of steel
Finishing
This stage is necessary for that, to bring the geometric and mechanical characteristics of the product to the required values.
The degree of change in the geometric parameters of the part when performing nitriding, as mentioned above, very insignificant, and it depends on such factors, as the thickness of the surface layer, which is saturated with nitrogen; temperature regime of the procedure. To guarantee almost complete absence of deformation of the processed product allows more advanced technology - ionic nitriding. When performing ion-plasma nitriding steel products are exposed to less heat, due to which their deformation is minimized.
In contrast to the innovative ion-plasma nitriding, traditional can be performed at temperatures, reaching 700 °. A replaceable muffle or muffle can be used for this purpose, built into the heating furnace. Use of a replaceable muffle, which machined parts are loaded in advance, before installing it in the oven, allows you to significantly speed up the nitriding process, but is not always an economically viable option (especially in those cases, when large products are processed).

Punch weighing more than 230 kg, subjected to nitriding treatment
Types of working environments
Different types of working media can be used to perform nitriding. The most common of these is the gaseous medium, consisting of 50% of ammonia and on 50% of propane or of ammonia and endogas, taken in the same proportions. The nitriding process in this medium is performed at a temperature of 570 °. The product is exposed to the gaseous medium during 3 hours. Nitrided layer, created using such a working environment, has a small thickness, but high strength and durability.
The method of ion-plasma nitriding has recently become widespread, performed in a nitrogen-containing dilute medium.

Ion-plasma nitriding - inside view
A distinctive feature of ion-plasma nitriding, which is also called glow discharge treatment, there is that, that the workpiece and the muffle are connected to an electric source, the product acts as a negatively charged electrode, and the muffle - in the role of positively charged. As a result, a stream of ions is formed between the part and the muffle - a kind of plasma, consisting of N2 or NH3, due to which there is a heating of the treated surface, and its saturation with the required amount of nitrogen.
In addition to traditional and ion-plasma nitriding, the process of saturating the steel surface with nitrogen can be performed in a liquid medium. As a working environment, which has a heating temperature of up to 570 °, in such cases a melt of cyanide salts is used. Nitriding time, performed in a liquid medium, can be from 30 to 180 minutes.




