
Inch thread: dimensions, table, GUEST
Дюймова різьба використовується переважно для створення з’єднань труб: її наносять як на самі труби, так і на металеві та пластикові фітинги, необхідні для монтажу трубних магістралей різного призначення. Основні параметри і характеристики різьбових елементів таких сполук регламентує відповідний ГОСТ, приводячи таблиці розмірів дюймової різьби, на які орієнтуються фахівці.

Сантехнічні вироби з трубної дюймової різьбленням
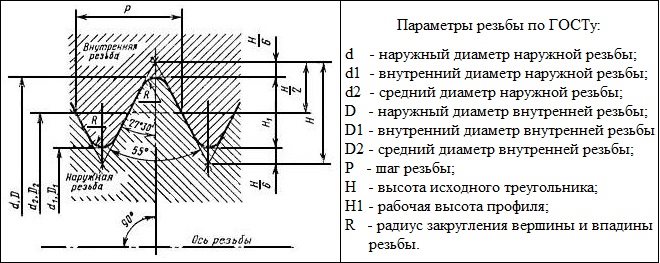
ОСНОВНІ ПАРАМЕТРИ
Regulatory document, в якому обумовлюються вимоги до розмірів циліндричної дюймової різьби, there is GOST 6111-52. Як і будь-яка інша, дюймова різьба характеризується двома основними параметрами: кроком і діаметром. Під останнім звичайно розуміють:
- outer diameter, вимірюваний між верхніми точками різьбових гребенів, що знаходяться на протилежних сторонах труби;
- внутрішній діаметр як величину, що характеризує відстань від однієї самої нижньої точки западини між різьбовими гребенями до іншого, також перебувають на протилежних сторонах труби.
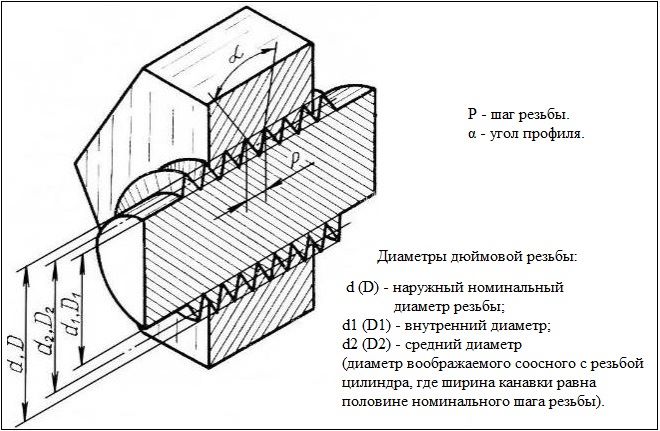
Знаючи зовнішній і внутрішній діаметри дюймової різьби, можна легко порахувати висоту її профілю. Для обчислення цього розміру достатньо визначити різницю між такими діаметрами.
Другий важливий параметр – крок – характеризує, на якій відстані один від одного розташовані два сусідніх гребеня або дві сусідні западини. На всій ділянці вироби, на якому виконана трубна різьба, її крок не змінюється і має одне і те ж значення. Якщо така важлива вимога не буде дотримано, вона буде просто неробочою, до неї не можна буде підібрати другий елемент створюваного з’єднання.
Ознайомитися з положеннями ГОСТ щодо дюймових різьб можна, by downloading the document in pdf format at the link below.
GUEST 6111-52 Різьблення конічна дюймова з кутом профілю 60°
Download
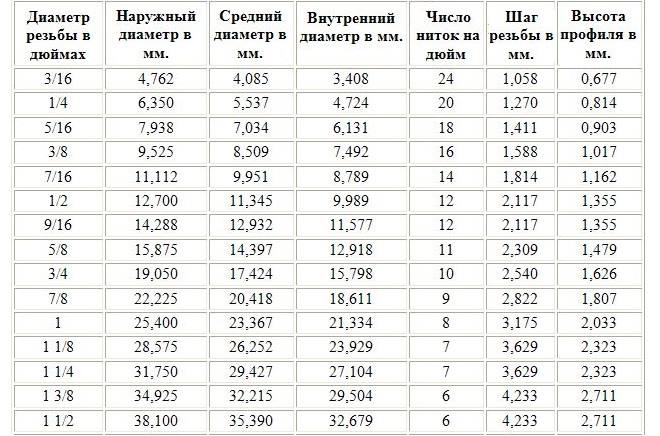
ТАБЛИЦЯ РОЗМІРІВ ДЮЙМОВИХ І МЕТРИЧНИХ РІЗЬБ
Learn, як співвідносяться метричні різьби з різними видами дюймових різьб, можна з допомогою даних з наведеної нижче таблиці.
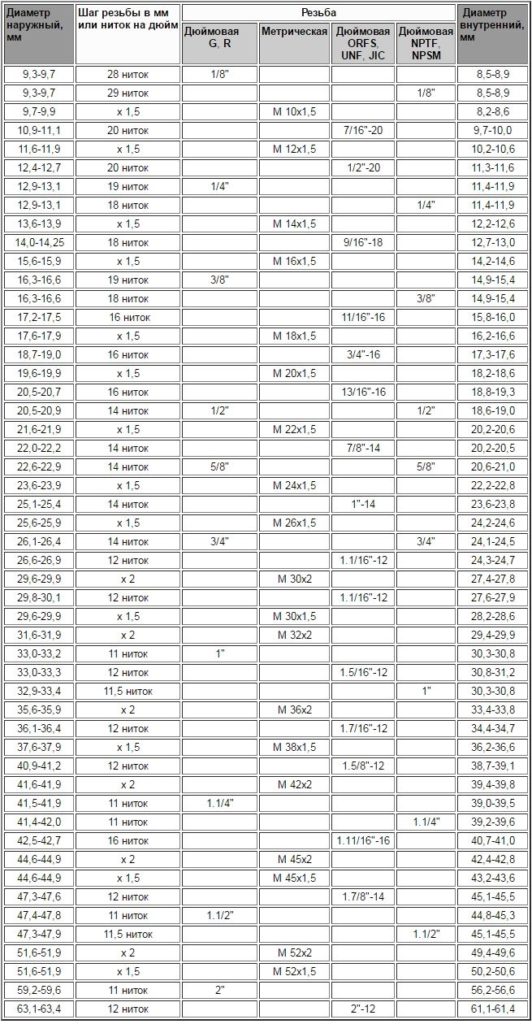
Подібні розміри метричних і різних різновидів дюймових різьб в діапазоні приблизно O8-64мм
ВІДМІННОСТІ ВІД МЕТРИЧНОЇ РІЗЬБИ
За своїми зовнішніми ознаками і характеристиками метричні і дюймові різьби мають не так багато відмінностей, до найбільш значущих з яких варто віднести:
- форму різьбового профілю гребеня;
- порядок розрахунку діаметра і кроку.
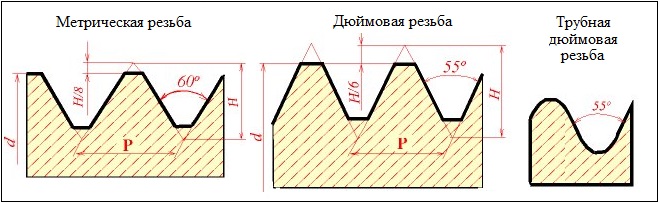
При порівнянні форм різьбових гребенів можна побачити, що у дюймової різьби такі елементи є більш гострими, ніж у метричній. Якщо говорити про точні розміри, то кут при вершині гребеня дюймової різьби становить 55°.
Параметри метричних і дюймових різьб характеризуються різними одиницями вимірювання. So, діаметр і крок перших вимірюються в міліметрах, а друге, in accordance, в дюймах. Trace, however, мати на увазі, що по відношенню до дюймової різьби використовується не загальноприйнятий (2,54 cm), а спеціальний трубний дюйм рівний 3,324 div. So, if, example, її діаметр становить ? in, то в перерахунку на міліметри він буде відповідати значенню 25.
Щоб дізнатися основні параметри дюймової різьби будь-якого типорозміру, який фіксується ГОСТом, достатньо заглянути в спеціальну таблицю. In the tables, що містять розміри дюймових різьб, наведені як цілі, так і дробові значення. It should be borne in mind, що крок у таких таблицях приводиться в кількості нарізаних канавок (thread), що містяться на одному дюймі довжини виробу.
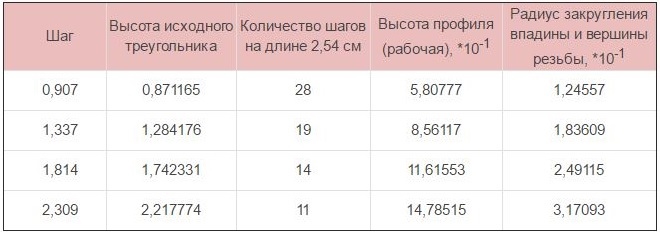
To check, чи відповідає крок вже виконаної різьблення розмірами, які обумовлює ГОСТ, цей параметр необхідно виміряти. Для таких вимірювань, що проводяться як для метричних, так і для дюймових різьб за одним алгоритмом, використовуються стандартні інструменти – гребінка, калібр, механічний вимірювач та ін.
Найпростіше виміряти крок трубної дюймової різьби з наступною методикою:
- В якості найпростішого шаблону використовують муфту або штуцер, параметри внутрішньої різьби яких точно відповідають вимогам, which provides GOST.
- Болт, параметри зовнішньої різьби якого необхідно виміряти, вкручується в муфту або штуцер.
- In that case, якщо болт сформував з муфтою або штуцером щільне різьбове з’єднання, diameter and pitch of the thread, яка нанесена на її поверхню, точно відповідають параметрам шаблону.

Крок дюймової різьби – це кількість витків на дюйм
Якщо ж гвинт не закручується у шаблон або вкручується, але створює з ним нещільне з’єднання, то слід провести такі вимірювання, використовуючи іншу муфту або інший штуцер. За аналогічною методикою вимірюється і внутрішня трубна різьба, тільки в якості шаблону у таких випадках застосовується виріб з зовнішньою різьбою.
Визначити необхідні розміри можна за допомогою резьбомера, що представляє собою пластину з щербинами, форма та інші характеристики яких точно відповідають параметрам різьблення з певним кроком. Така пластина, яка виступає в ролі шаблону, просто прикладається до перевіряється різьбі своєї зазубреною частиною. About that, що різьба на людину елементі відповідає необхідним параметрам, буде свідчити щільне прилягання до її профілю зазубреною частини пластини.
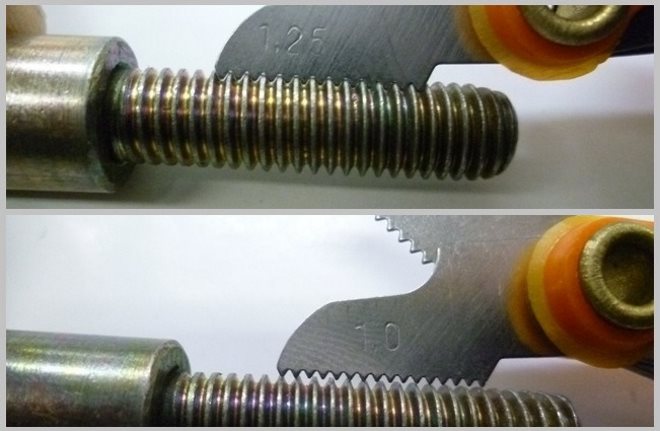

Для того щоб виміряти розмір зовнішнього діаметра дюймової або метричної різьби, можна використовувати звичайний штангенциркуль або мікрометр.
ТЕХНОЛОГІЇ НАРІЗКИ
Різьба трубна циліндрична, яка відноситься до дюймовому типу (як внутрішня, так і зовнішня), може нарезаться ручним або механічним методом.
Нарізка різьби вручну
Нарізування різьби за допомогою ручного інструменту, в якості якого використовується мітчик (для внутрішньої) або плашка (для зовнішнього), виконується в кілька кроків.
- Оброблювана труба затискається в лещатах, а використовуваний інструмент фіксується у воротку (мітчик) або в плашкодержателе (плашка).
- Плашка надівається на кінець труби, а мітчик вставляється у внутрішню частину останньої.
- Використовуваний інструмент укручується в трубу або нагвинчує на її кінець допомогою обертання воротка або плашкодержателя.
- Щоб зробити результат більш чистим і точним, можна повторити процедуру нарізування кілька разів.
Механічним способом трубна різьба нарізається за наступним алгоритмом:
- Оброблювана труба затискається в патроні верстата, на супорті якого фіксується різьбонарізний різець.
- На кінці труби, використовуючи різець, знімають фаску, після чого виконують налаштування швидкості переміщення супорта.
- Після підведення різця до поверхні труби на верстаті включають різьбову подачу.
It should be borne in mind, що дюймова різьба нарізається механічним методом за допомогою токарного верстата тільки на трубних виробах, товщина і жорсткість яких дозволяють це зробити. Виконання трубної дюймової різьби механічним способом дозволяє отримувати якісний результат, але застосування такої технології вимагає від токаря відповідної кваліфікації та наявності певних навичок.
КЛАСИ ТОЧНОСТІ І ПРАВИЛА МАРКУВАННЯ
Різьблення, що відноситься до дюймовому типу, as indicated by GOST, може відповідати одному з трьох класів точності – 1, 2 and 3. Поруч з цифрою, яка позначає клас точності, ставлять літери «А» (зовнішня) або «В» (внутрішня). Повні позначення класів точності різьби в залежності від її типу виглядають як 1А, 2А і 3А (для зовнішніх) і 1В, 2В і 3В (для внутрішніх). It should be borne in mind, що 1-го класу відповідають самі грубі різьби, а 3-го – найбільш точні, розмірами до яких пред’являються дуже жорсткі вимоги.
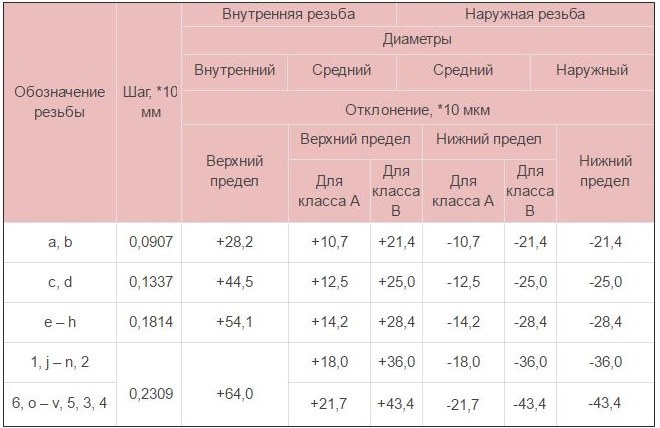
To understand, яким параметрам відповідає конкретний різьбовий елемент, достатньо розібратися в позначенні різьби, яка на нього нанесено. Позначення, про який йде мова, використовують багато зарубіжні виробники, які працюють за американськими стандартами, належать до елементів нарізних з’єднань.
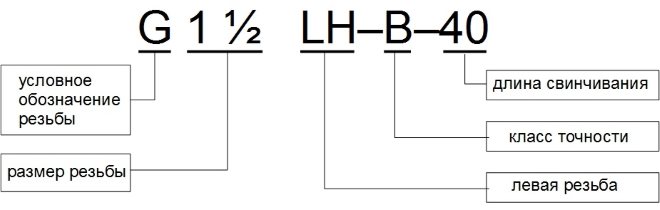
У такому маркуванню міститься наступна інформація про різьбі:
- номінальний розмір (outer diameter) – перші цифри;
- число витків, що припадає на дюйм довжини;
- group;
- accuracy class.
В позначенні дюймової різьби також можуть бути присутні букви LH, which indicate that, що її витки не мають права, а ліве напрямок.




