
Chrome plating of details - a decorative covering with chrome: technology
The term "steel" can be understood as the diffusion saturation of the surface of the processed product with a layer of chromium, and the application of chromium by galvanic technology. There is also a more general term - "metallization". By this is meant the application of a layer of metal on the treated surface, in the role of which may be including chrome.

True chrome-plating fans don't mind chrome-plating everything, as much as possible
Among the methods of applying galvanic metal chromium coating is the most popular. That is why the term "metallization" is often used as a synonym for the word "steel"..
What do you need a chrome layer
The application of a layer of chromium can be performed to improve the decorative characteristics of metal products (decorative chrome plating), as well as to protect the metal part from corrosion and give its surface greater hardness. So, due to chrome plating it is possible not only to improve mechanical and decorative characteristics of a product, but also significantly extend its service life.
Many different chrome products can be found at home, and in various industries. Use of metal products, on the surface of which a layer of chromium is applied, relevant in those cases, when they will be operated in the conditions of constant influence of aggressive environments and intensive friction.

Restoration of a chromeplated covering returns to former appearance and prolongs service life of a design
The following products with a chromeplated covering are most actively used in household conditions:
- furniture accessories;
- elements for home and office interiors;
- car wheels and vehicle parts;
- souvenir products;
- plumbing equipment.

Chrome gas tank
In industry, chrome plating technology is used for the following purposes:
- in the manufacture of products from powder technology;
- in the manufacture of molds, which are used for the manufacture of rubber products and polymeric materials;
- in the manufacture of reflectors for various purposes;
- to increase the hardness of the surface layer and the wear resistance of the cutter, as well as a special measuring instrument;
- to give exceptional decorative characteristics to the body and other parts of vehicles;
- for processing of details, operated under conditions of constant friction and negative environmental influences (elements of steam equipment and heating networks, details of automobile engines and ships).

Industrial galvanic line, is intended for drawing firm chromium on products from steels and non-ferrous metals
Chrome parts have the following characteristics:
- high corrosion resistance;
- microhardness, indicators of which reach values 950-1100 units on the HV scale;
- high porosity of the coating, its wear - and heat resistance;
- low coefficient of friction of the formed coating;
- large scatter of the thickness of the chrome layer (5-300 microns and even more).
Listed characteristics, which can be achieved by chrome-plating steel and other metals, makes such technology so popular. List all areas, where the chrome plating process is actively used, can be long enough.
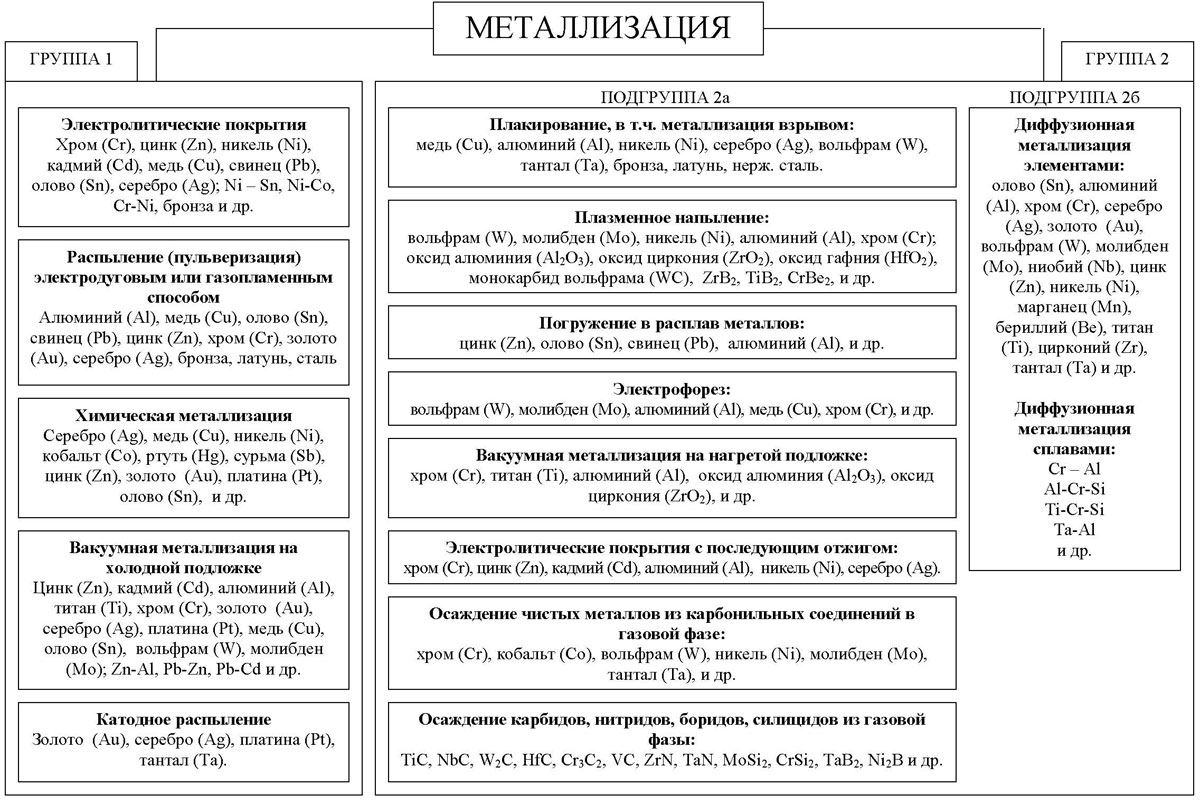
Varieties of metallization by the method of interaction of the metallized surface with the applied metal (click to enlarge)
Basic methods
To date, there are the following types of chrome plating, each of which has its advantages and disadvantages:
- chrome plating, which is performed by galvanic technology;
- diffusion chromium plating, carried out in an airtight container at high temperature;
- vacuum chrome plating, requires the use of a special camera, in which a vacuum is created;
- catalytic chromium plating, assumes, that on a surface of the processed product special liquids without acids are put;
- chemical chrome plating of steel and other metals, which on technology of execution reminds usual painting;
- chrome plating with galvanic technology.
Electroplating
Coating, obtained by galvanic chromium plating, can be of several types.
"Solid chrome"
Coating of this type is carried out using current, characterized by high density (more 100 A / dm2). The temperature of the electrolytic solution should not exceed 40 °. A layer of chrome, applied by this technology, which makes the surface of the product harder, but at the same time more fragile.
"Brilliant chrome"
Coatings of this type are applied using current, whose density is in the range 30-100 A / dm2 and in solution with a temperature in the range of 45-60 °. Surface layer of metal, on which the chrome coating is applied by this technology, acquires exceptionally high hardness and wear resistance, as well as mirror gloss.
"Milk chrome"
Minimum current is used to obtain chrome-plated coatings of this type (to 25 A / dm2). This method of chrome plating of details does not allow to receive on them a covering of high hardness. A layer of chrome, applied to the surface of the product in such cases, resembles a very elastic mass, in the structure of which there are almost no pores.
To perform such chromium plating, trivalent or hexavalent chromium is required. Chromic anhydride is used as the main component of the electrolytic solution in the chromium plating of metal using trivalent chromium.. When using hexavalent chromium, chromium chloride or sulfate acts as an element.
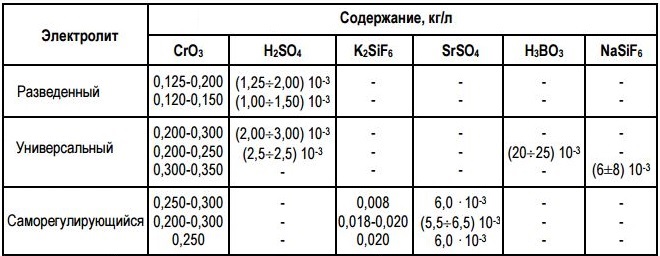
Compositions of electrolytes for chromium plating
Solutions, made on the basis of hexavalent chromium, contain the following components:
- sulfuric acid - 2.25-3 g / l;
- chromium anhydride - 225-300 g / l;
- lead, which is usually part of the anode in combination with antimony or tin, – 4-6%.
Of great importance for the quality of the applied chrome coating is the proportion of sulfuric acid and chromic anhydride in the electrolytic solution used. Usually, such a ratio is trying to maintain within 1:100. If it is less, then the surface of the chrome-plated part will not be of high quality, peeling may occur on it, opacity and various stains. Example, if an electrolytic solution is used for chromium plating, in which sulfuric acid and chromic anhydride are contained in the ratio 1:50, then the chrome coating will not get a high enough opacity and scattering capacity.
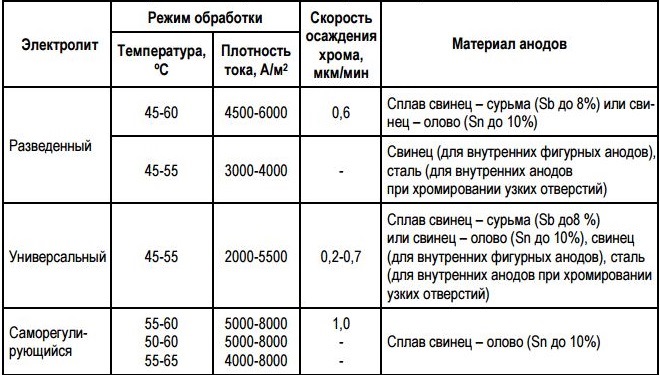
Chromium modes and materials for anodes
Electric current density is also an important parameter when applying a chrome coating (not higher 310 kA / dm2) and the temperature of the electrolytic solution (45-60°). If you increase the current density, then on the corner and end elements of the chrome-plated part can be formed dendrites, which significantly impair the decorative characteristics of the product.
In addition to lead anodes, the chemical composition of which is supplemented by antimony (not more 6%), Titanium anodes are used today for chrome plating, covered with a platinum layer. When chromium plating, it is desirable not to use soluble anodes: for the manufacture of such elements it is better to use sheets or rods of metal, the cross section of which is approximately 1,5 cm.
Special contact devices are used to immerse the products in the bath
Chrome anodes, made of lead, must be cleaned regularly with a metal brush, as on their surface the chromic-acid plaque is constantly formed. In that case, if titanium anodes are used for chromium deposition, covered with a layer of platinum, such cleaning will not be required. If the anodes, by means of which chrome plating of products from steel and other metals is carried out, do not apply for several days, they must be removed from the electrolytic solution and kept in water all this time.
How to prepare a product
Decorative chrome plating technology (as well as the application of a layer of chromium for protective purposes) involves careful preparation of the product. Such training consists in performing such procedures, as:
- grinding of the processed surface, as well as its thorough polishing;
- washing the product and wiping it with a soft cloth;
- isolation of those parts of the surface, where chrome plating is not required;
- degreasing the chrome-plated part;
- pickling of the product, which improves the adhesion of the applied chrome layer with the base metal;
- placement of the product in the electrolytic solution with a special bracket.

Grinding the product before chrome plating
In some cases, the technology of decorative chrome plating involves pre-etching the treated surface and applying a layer of other metal (copper or nickel), which helps to increase the strength of the chrome coating.
How to carry out the chrome plating procedure
The technology of decorative chrome plating is as follows.
- The product after preliminary preparation is placed in a container with electrolytic solution, in which the anode is already located.
- Solution, in which the product is immersed, must be preheated to the desired operating temperature. It should be borne in mind, that the operating temperature of the electrolytic solution must be maintained throughout the chromium plating process. This is necessary for that, to ensure good adhesion of the alluvial layer, as well as its homogeneity in structure and thickness.
- Depending on that, how thick the chrome layer should be, determine the residence time of the product in the electrolytic solution.
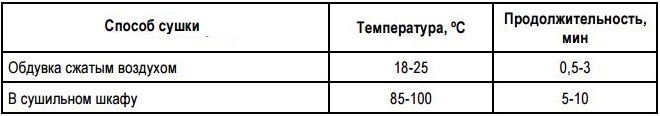
Recommended modes of drying chrome-plated products
Decorative chrome plating technology also involves heat treatment of the part (this stage is necessary for that, to make the chrome coating harder and stronger). Product, on the surface of which is applied a layer of chromium, incubated for several hours in a heating furnace at a temperature of about 200 °.
The video below shows in detail the process of galvanic chrome plating with comments in the form of subtitles.
Chemical method
Currently, the technology of decorative chrome plating is actively used, does not involve the use of electrolytic solution. In this manner, the essence of which is, that the chromium from the working solution settles on the surface of the workpiece, chrome plating of aluminum and other metals is performed, as well as parts made of polymeric materials.
Working solution, used to perform such chrome plating, is prepared on the basis of chromium-containing reagent, distilled water and sodium hypophosphite. In the process of chrome plating, which is exposed to aluminum or any other alloy, sodium hypophosphite restores chromium from its salts, and the metal settles in a thin layer on the surface of the workpiece. Due to that, used to perform such chromium plating chemical reagents contain phosphorus, ready chrome layer, partially saturated with this element, has a fairly high strength.
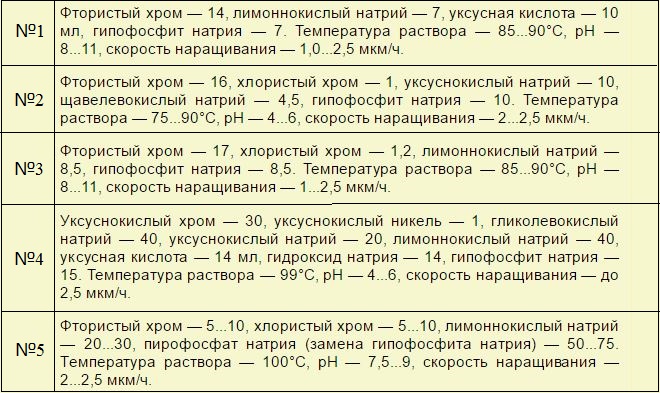
Compositions of solutions for chemical chromium plating
The chemical method of applying a chrome coating is not only easy to implement, but also greater environmental safety, if you compare it with other chrome plating technologies. This way, with which you can chrome aluminum, steel and even polymeric materials, used even at home.
Performing chrome plating of car parts or other products of chemical technology, should be borne in mind, that the finished coating is matte and has an unattractive grayish hue. To give such a coating a characteristic chrome shine, it is necessary to carry out finishing polishing.
With the help of chrome plating products made of various metals and polymeric materials can provide not only protective properties, but also exceptional decorative characteristics. Example, application of black chrome on various details is possible, the coating from which makes their appearance spectacular and presentable.




