Steel grades - decoding, marking, table
To any specialist, dealing with metal, familiar concept of "steel grade". Deciphering the labeling of steel alloys makes it possible to get an idea of their chemical composition and physical characteristics. Understand this labeling, despite its complexity, quite simply - it is important only to know, on what principle it is composed.

Rare production does without steel, therefore it is extremely important to understand its brands
Denote the alloy by letters and numbers, by which you can accurately determine, what chemical elements it contains and in what quantity. Knowing this, as well as that, how each of these elements can affect the finished alloy, can be determined with a high degree of probability, what are the technical characteristics of a particular steel grade.
Types of steels and features of their marking
Steel is an alloy of iron and carbon, while the content of the latter in it is not more 2,14%. Carbon adds hardness to the alloy, but with its excess the metal becomes very brittle.
One of the most important parameters, according to which steels are divided into different classes, there is a chemical composition. Among the steels according to this criterion are alloyed and carbon, the latter are divided into few- (carbon to 0,25%), on average- (0,25–0,6%) and high carbon (they contain more 0,6% carbon).

Varieties of steels
Including alloying elements in steel, it can be given the necessary characteristics. That's how it is, combining the form and quantitative content of additives, receive stamps, have improved mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, magnetic and electrical characteristics. Of course, it is possible to improve characteristics of steels and by means of heat treatment, but alloying additives allow you to do it more effectively.
According to the quantitative composition of alloying elements distinguish low-, medium and high alloy alloys. In the first alloying elements no more 2,5%, in medium-alloyed - 2.5-10%, high-alloy - more 10%.
Classification of steels is carried out according to their purpose. So, distinguish instrumental and structural types, stamps, differing in special physical properties. Tool types are used for the production of stamps, measuring, as well as cutting tools, constructional - for production, which is used in construction and mechanical engineering. From alloys, which have special physical properties (also called precision), make products, which must have special characteristics (magnetic, strength, etc.).

Classification of steels by purpose
Steels are opposed to each other and on special chemical properties. Alloys of this group include stainless, scale-resistant, heat-resistant, etc.. What is characteristic, stainless steels can be corrosion resistant and stainless food - these are different categories.
In addition to useful elements, steel contains harmful impurities, the main of which are sulfur and phosphorus. It also contains unbound gases (oxygen and nitrogen), which negatively affects its characteristics.
If we consider the main harmful impurities, then phosphorus increases the brittleness of the alloy, especially strong at low temperatures (so-called cold brittleness), and sulfur causes cracks in the metal, heated to high temperature (red fragility). Phosphorus, to everything else, significantly reduces the ductility of the heated metal. According to the quantitative content of these two elements, steels of ordinary quality are distinguished (not more than 0.06-0.07% of sulfur and phosphorus), quality (to 0,035%), high quality (to 0,025%) and especially high quality (sulfur - to 0,015%, phosphorus - to 0,02%).
The marking of steels also indicates that, to what extent oxygen is removed from their composition. According to the level of deoxidation, steels are distinguished:
- quiet type, are denoted by the letter combination "SP";
- semi-calm - "PS";
- boiling - "KP".
What does the marking of steels
It became quite easy to decipher the brand, you only need to have certain information. Structural steels, which have the usual quality and do not contain alloying elements, marked with the letter combination "Century". By figure, following the letters in the brand name, can be determined, how much carbon in such an alloy (calculated in tenths of a percent). The numbers can be followed by the letters "KP": from them it becomes clear, that this alloy is not completely deoxidized in the furnace, in accordance, it belongs to the category of boiling. If the brand name does not contain such letters, then the steel corresponds to the category of calm.

Chemical composition of carbon structural steels of ordinary quality
Structural unalloyed steel, belonging to the category of quality, has two digits in its designation, it determines the average carbon content (calculated in hundredths of a percent).
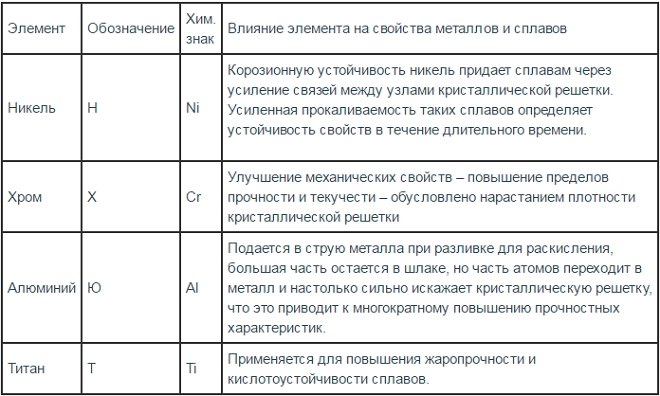
Before we begin to consider those grades of steel, which contain alloying additives, it is necessary to understand that, how these additives are denoted. The marking of alloy steels may include the following letter designations:

List of used alloying additives
Designation of steels with alloying elements
As mentioned above, classification of steels with alloying elements includes several categories. Marking of alloy steels is made according to certain rules, knowledge of which allows you to easily determine the category of a particular alloy and the main area of its application. In the initial part of the names of such brands are numbers (two or one), showing the carbon content. Two figures indicate its average content in the alloy in hundredths of a percent, and one in tenths. There are also steels, that do not have the number of the brand name at the beginning. This means, that the carbon in these alloys is contained within 1%.
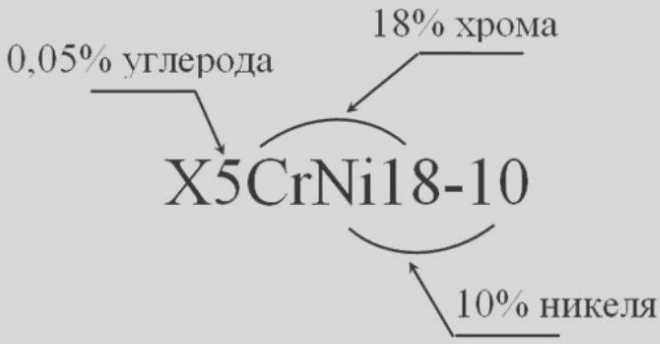
Example of alloy steel marking
Letters, which can be seen by the first digits of the brand name, indicate that, what this alloy consists of. Behind the letters, giving information about a particular element in its composition, numbers may or may not stand. If the number is, then it is determined by it (as a percentage) the average content of the letter specified in the alloy, and if there is no figure, means, this element is contained within 1 to 1,5%.
At the end of the marking of certain types of steel may be the letter "A". That says it all, that we have high-quality steel. Such grades may include carbon steels and alloys with alloying additives in their composition. According to the classification, this category of steels includes those, in which sulfur and phosphorus are not more 0,03%.
Examples of marking steels of different types
Determining the grade of steel and classifying the alloy as a certain type is a task, which should not cause any problems to the specialist. A table is not always at hand, which gives a transcript of brand names, but examples will help to understand this, which are listed below.
The content of elements in common steel grades (click to enlarge)
Structural steels, which do not contain alloying elements, are denoted by the letter combination "Century". Figures, following, Is the carbon content, calculated in hundredths of a percent. Low-alloy structural steels are marked somewhat differently. Example, in steel of the 09G2S brand 0,09% carbon, and alloying additives (manganese, silicon and others) contained in it within 2,5%. Very similar in their labeling 10HSND and 15HSND differ in the amount of carbon, and the share of each alloying element in them is not more 1%. That is why after the letters, denoting each alloying element in such an alloy, not worth any numbers.
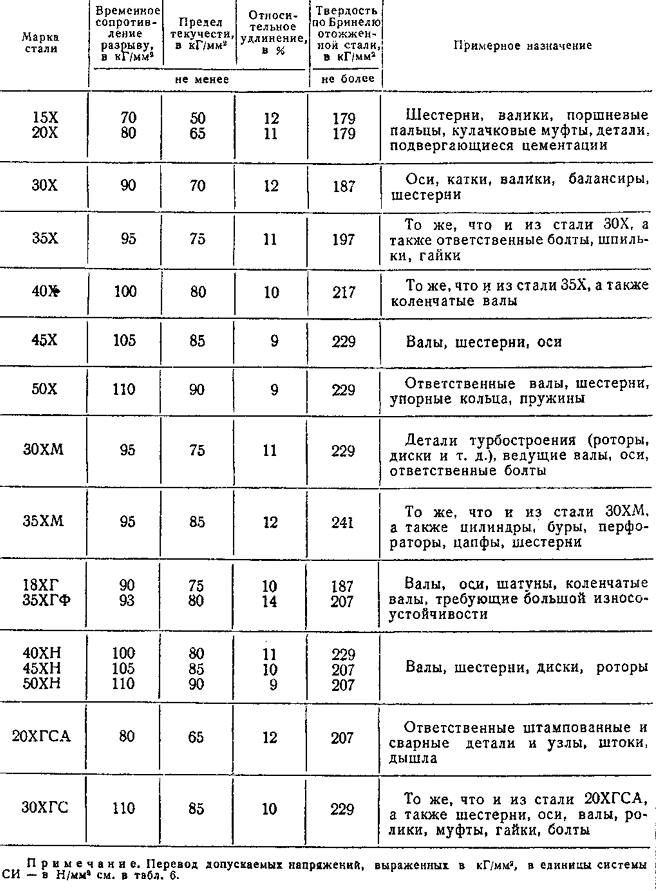
20X, 30X, 40X and others. - this is how structural alloy steels are marked, the predominant alloying element is chromium. The number at the beginning of such a mark is the carbon content in the alloy in question, calculated in hundredths of a percent. The letter designation of each alloying element can be marked with a number, on which determine its quantitative content in the alloy. If it is not there, then the specified element in steel contains no more 1,5%.
You can consider an example of the designation of chromium-manganese steel 30HGSA. She, according to the labeling, consisting of carbon (0,3%), manganese, silicon, as well as chromium. Each of these elements contains in the range of 0.8-1.1%.
How to decipher steel marking?
That deciphering of designation of various types of steels did not cause difficulties, should be well known, what they are. Certain categories of steels have special markings. They are usually denoted by certain letters, which allows you to immediately understand the purpose of the metal, and its approximate composition. Consider some of these brands and understand their designation.
Properties and purposes of structural alloy steels
Structural steels, specially designed for the manufacture of bearings, can be found by the letter "W", this letter is placed at the very beginning of their marking. After it in the name of the brand there is a letter designation of the corresponding alloying additives, as well as figures, by which the quantitative content of these additives is known. So, in steels of grades SHX4 and SHX15, except iron and carbon, chromium is contained in quantity 0,4 and 1,5%, in accordance.
The letter "K", which stands after the first digits in the brand name, report the quantitative carbon content, denote structural non-alloy steels, used for the production of vessels and steam boilers, working under high pressure (20TO, 22K and others).
High-quality alloy steels, which have improved casting properties, can be found by the letter "L", standing at the very end of the marking (35ХМЛ, 40HL and others).
Some difficulty, if you do not know the features of the label, may cause decoding of construction steel grades. Alloys of this category are denoted by the letter "C", which is put in the beginning. Figures, following her, indicate the minimum yield strength. Such stamps also use additional letters:
- letter T - heat-strengthened rolled metal;
- letter K - steel, characterized by high corrosion resistance;
- letter D - alloy, characterized by high copper content (С345Т, C390K and others).
Unalloyed steel, belonging to the category of instrumental, denoted by the letter "U", it is affixed at the beginning of their marking. Number, following this letter, expresses the quantitative content of carbon in the alloy. Steels of this category can be high quality and high quality (they can be identified by the letter "A", it is placed at the end of the brand name). Their marking may contain the letter "P", which means high manganese content (U7, U8, У8А, U8GA and others).
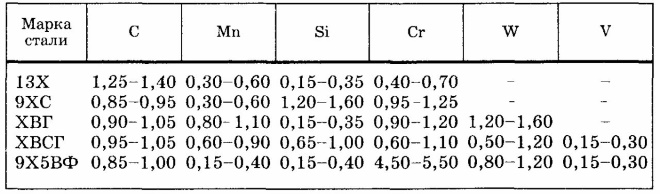
Tool steels, containing alloying elements in its composition, are marked similarly to doped structural (HVG, 9HVG and others).
The composition of alloy tool steels (%)
Marking of those steels, which fall into the category of high-speed, starts with the letter "P", followed by numbers, indicating the quantitative content of tungsten. Otherwise, the brands of such alloys are called according to the standard principle: letters, denoting the element, and, in accordance, figures, reflecting its quantitative content. Chromium is not indicated for such steels, since its standard content in them is about 4%, as well as carbon, the amount of which is proportional to the vanadium content. If the amount of vanadium exceeds 2,5%, then its letter designation and quantitative content are affixed at the very end of the marking (З9, Р18, P6M5F3 and others).
The effect of some additives on the properties of steel
Non-alloy steels are specially marked, belonging to the category of electrical (they are often called pure technical iron). Low electrical resistance of such metals is provided due to that, that their composition is characterized by a minimum carbon content - less 0,04%. There are no letters in the designation of such steels, only numbers: 10880, 20880 etc. The first digit indicates the classification by type of processing: hot rolled or forged - 1, calibrated - 2. The second figure is related to the category of the aging factor: 0 - unregulated, 1 - normalized. The third digit indicates the group, to which this steel belongs according to the normalized characteristic, taken as the main. The fourth and fifth digits determine the value of the normalized characteristic.
Principles, for which the designation of steel alloys, were developed in the Soviet period, but still successfully used not only in Russia, but also in the CIS countries. Possessing information about a particular brand of steel, it is possible not only to determine its chemical composition, but also to effectively select metals with the required characteristics.
It is important to understand this issue as specialists, who develop and design various metal structures, and so on, who often works with different steels and is engaged in the manufacture of parts for different purposes.