Copper ore - copper mining, refinement, deposits
Copper, actively used in almost all industries, extracted from various ores, the most common of which is bornite. The popularity of this copper ore is due not only to the high content of copper in its composition, but also significant reserves of bornite in the bowels of our planet.

native copper
Copper ore deposits
Copper ores are accumulations of minerals, in which, except copper, contains other elements, forming their properties, in particular nickel. Those types of ores are included in the category of copper, in which this metal contains such an amount, that it was economically feasible to extract by industrial methods. Ores satisfy such conditions, the copper content of which is within 0,5-1%. Our planet has a supply of copper-containing resources, the main part of which (90%) are copper-nickel ores.
Most of Russia's copper ore reserves are in Eastern Siberia, ??on the Kola Peninsula, in the Ural region. Chile is on the list of leaders in the total reserves of such ores, deposits are also being developed in the following countries: USA (porphyry ore), Kazakhstan, Zambia, Poland, Canada, Armenia, Zaire, Peru (porphyry ore), Congo, Uzbekistan. Experts have counted, that in large deposits of all countries copper in total contains about 680 million tons. Naturally, question about, how copper is mined in different countries, must be considered separately.

covellin
All copper ore deposits are divided into several categories, differing in genetic and industrial-geological characteristics:
- stratiform group, presented ??copper shales and sandstones;
- ores of pyrite type, which include native and vein copper;
- hydrothermal, including ores, called copper-porphyry;
- igneous, which are the most common ores of the copper-nickel type;
- ore skarn type;
- carbonate, represented by ores of iron-copper and carbonatite type.
In Russia, copper is mined mainly in shale and sand deposits, in which the ore is contained in copper pyrite, copper-nickel and copper-porphyry forms.

bornite
Natural compounds with copper content
Pure copper, which are its nuggets, presented ??in nature in very small quantities. Basically, copper is present in nature in the form of various compounds, the most common of which are the following.
- Bornite is a mineral, which was named after a scientist from the Czech Republic I. Bourne. This is a sulfide ore, the chemical composition of which is characterized by its formula - Cu5FeS4. Bornit has other names: stringatium pyrite, copper purple. In nature, this ore is represented ??in two polymorphic species: low-temperature tetragonal-scalenohedral (the temperature is lower 228 degrees) and high-temperature cubic-hexaoctahedral (more 228 degrees). This mineral can have different types and depending on its origin. So, exogenous bornite is a secondary early sulfide, which is very unstable and easily destroyed by weathering. The second type - endogenous bornite - is characterized by instability of chemical composition, in which chalcocine may be present, galena, sphalerite, pyrite and chalcopyrite. Theoretically, the minerals of these species may include from 25,5% sulfur, over 11,2% iron and more 63,3% copper, but in practice such content of these elements is never sustained.
- Chalcopyrite is a mineral, the chemical composition of which is characterized by the formula CuFeS2. Chalcopyrite, having a hydrothermal origin, formerly called copper pyrite. Along with sphalerite and galena, it belongs to the category of polymetallic ores. This mineral, which, except copper, contains iron and sulfur, formed as a result of metamorphic processes and may be present in two types of copper ores: contact-metasomatic species (skarni) and mountain metasomatic (greyhounds).
- Chalcozin is a sulfide ore, the chemical composition of which is characterized by the formula Cu2S. This ore contains a significant amount of copper (79,8%) and sulfur (20,2%). This ore is often called "copper luster"., due to that, that its surface looks like a gleaming metal, which has different shades - from lead gray to completely black. In copper-containing ores, chalcocine looks like dense or fine-grained inclusions.

chalcopyrite
In nature, there are rarer minerals, which contain copper.
- Cuprite (Cu2O), relating to minerals of the oxide group, can often be found in places, where there is malachite and native copper.
- Covellin is a sulfide rock, formed by metasomatic means. For the first time this mineral, the copper content in which is 66,5%, was discovered at the beginning of the last century in the vicinity of Vesuvius. Now covellin is actively mined in fields in such countries, as the United States, Serbia, Italy, Chile.
- Malachite is a mineral, well known to all as a stone. Probably everyone has seen products from this beautiful mineral in the photo or even own them. Malachite, which is very popular in Russia, - this is copper carbonate greens or copper dihydrococcarbonate, belonging to the category of polymetallic copper-containing ores. The malachite found testifies to that, that there are deposits of other minerals nearby, containing copper. In our country, a large deposit of this mineral is located in the Nizhny Tagil region, previously it was mined in the Urals, but now its reserves there are much depleted and not developed.
- Azurite is a mineral, which because of its blue color is also called "copper blue". It is characterized by hardness 3,5-4 units, its main deposits are being developed in Morocco, Namibia, Congo, England, Australia, France and Greece. Azurite is often fused with malachite and occurs in those places, where nearby are deposits of copper-containing ores of the sulfide type.

Copper production technologies
To extract copper from minerals and ores, which we talked about above, three technologies are used in modern industry: hydrometallurgical, pyrometallurgical and electrolysis. Pyrometallurgical method of copper enrichment, which is the most common, uses chalcopyrite as raw material. This technology involves several consecutive operations. At the first stage, copper ore is enriched, for which oxidative calcination or flotation is used.
The flotation method is based on that, that the empty rock and its parts, which contain copper, wet in different ways. When placing the entire mass of rock in a bath of liquid composition, in which air bubbles are formed, and its part, which contains mineral elements, transported by these bubbles to the surface, stick to them. As a result, on the surface of the bath collects concentrate - rough copper, in which this metal is contained from 10 to 35%. It is from this powdered concentrate and further production of pure copper.
Oxidative firing looks a little different, with which to enrich copper ores, containing a significant amount of sulfur. This technology involves heating the ore to a temperature 700-8000, as a result of which sulfides are oxidized and the sulfur content in copper ore is reduced almost twice. After such firing, the enriched ore is melted in chops or shaft furnaces at a temperature 14500, resulting in a matte alloy, consisting of sulfides of copper and iron.
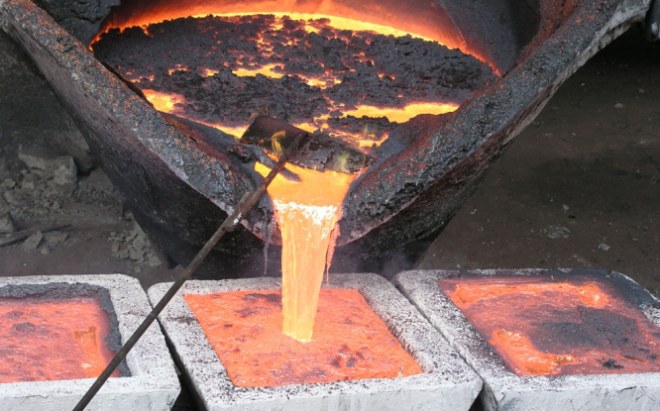

Pouring copper by mold
The properties of the obtained matte should be improved, for this purpose it is blown in horizontal converters without supply of additional fuel. As a result of such lateral blowing, iron and sulfides are oxidized, iron oxide is converted into slag, and sulfur - in SO2.
Rough copper, resulting from such a process, contains to 91% of this metal. To make the metal even cleaner, it is necessary to refine copper, for which it is necessary to remove impurities. This is achieved through the technology of fire refining and acidified solution of copper sulfate. This refining of copper is called electrolytic, it allows you to get the metal with purity 99,9%.
There is also a hydrometallurgical method of copper enrichment, which involves leaching the metal with sulfuric acid. As a result of such leaching, a solution is obtained, from which then and emit copper and other metals, including precious. This technology is used for ore beneficiation, which are characterized by a very low content of copper in its composition.




