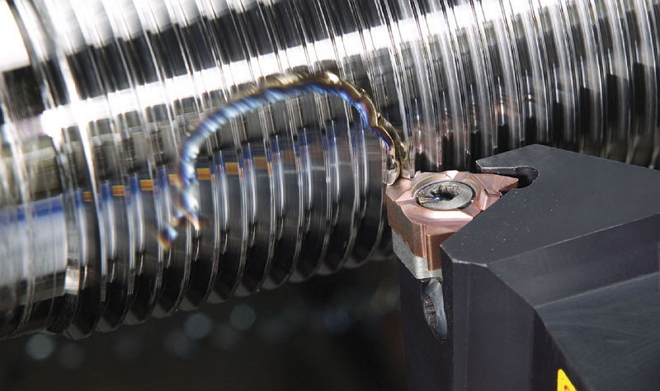
Threading on a lathe with a cutter and other tools
Threading on a lathe refers to those operations, for which various tools can be used. This problem is most often solved with the help of a cutter. In addition, taps are also used, dice, working heads of special purpose. in addition, on lathes such operation can be performed by knurling technology.

The process of cutting a thread on a lathe cutter
Threading using turning equipment
When cutting threads on the workpiece, mounted on a lathe, using a cutter, this process is as follows: tool, moving along the axis of the rotating part (feed movement), with its pointed tip draws a line of helical type on its surface. A characteristic parameter of the helix, formed by the cutter on the surface of the workpiece, there is an angle of its rise or increase. The magnitude of this angle, measured between tangents, located to the helix, and plane, which is perpendicular to the axis of rotation of the part, determined:
- the feed rate of the cutting tool, moving along the axis of the workpiece;
- frequency, with which the part rotates.
No less important parameter of the helix is its pitch, which characterizes the distance between its adjacent turns. It is measured along the axis of the workpiece.
Moving along the axis of the rotating workpiece, the cutter cuts into it and creates a twisted surface, which is commonly called carving. Elements with a threaded surface are used to solve various problems: ensuring the movement of elements relative to each other, their articulation and sealing of molded joints.
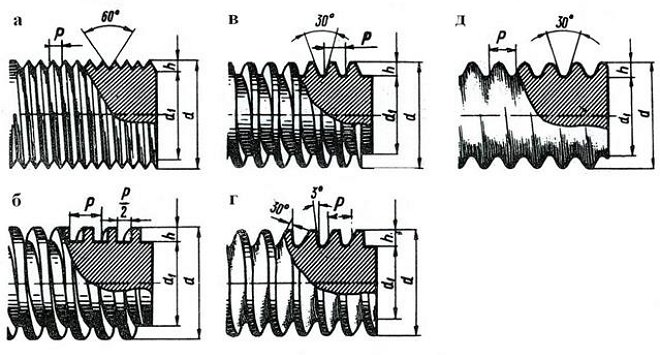
The most common types of thread profile: and - triangular, b - rectangular, in - trapezoidal, d - persistent, e - round
The surface of the threaded workpiece can be cylindrical and conical. The characteristics of the threaded connection are significantly influenced by the thread profile, that is, its contour in the plane. Highlight profiles:
- triangular;
- trapezoidal;
- rectangular;
- persistent;
- round.
The thread on the surface of the part can be formed by a single helical thread (single-pass) or several (multitasking). If you cut a few spiral threads, then they are placed equidistantly in relation to each other.
You can count the number of threads at the beginning of the threaded surface. Multi-threaded carving, except step, characterized by this parameter, as a move. This is the distance, measured between two identical points of two adjacent turns, which are formed by a single thread. This distance is measured along the line, located parallel to the axis of the threaded part. In one-way carving, formed by a single thread, the course is equal to the step, and for multi-western it can be calculated, if you multiply the step by the number of events.
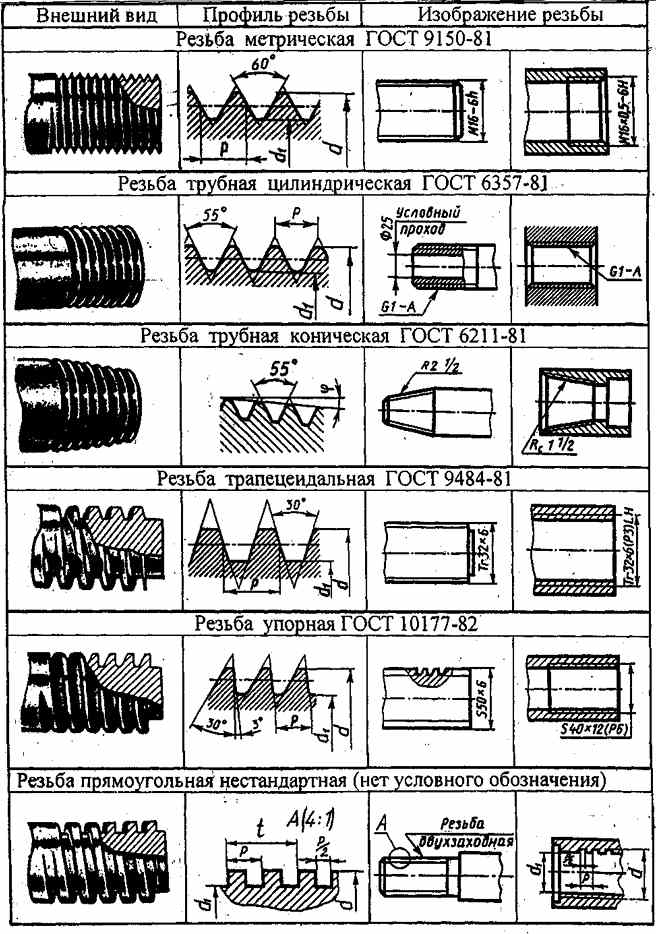
All kinds of carvings with schemes, parameters and regulating their GOST
use of incisors
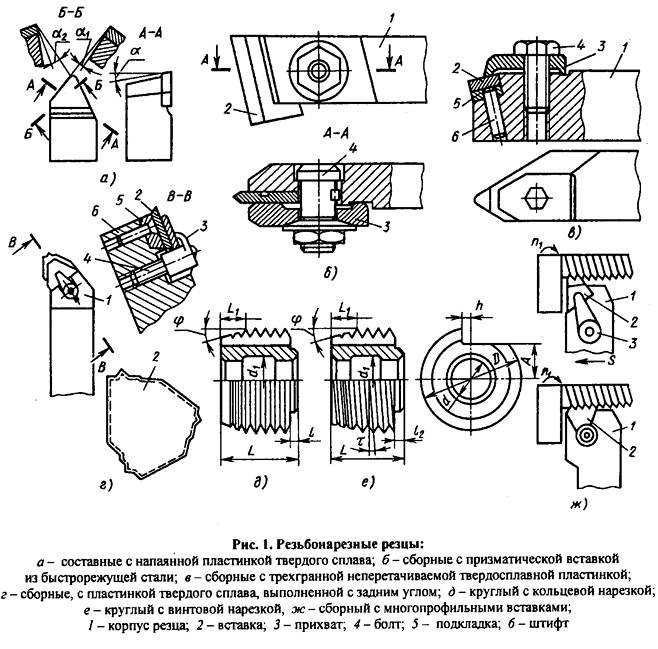
Thread cutters are required to cut the thread with a lathe. They are made of high-speed steel, and the requirements for their characteristics are determined by the relevant standard (18876-73). By design, such cutters are divided into the following types:
- prismatic;
- rod;
- round (disk).
Screw threaded groove on the surface of the workpiece is cut with a cutter bent or straight shape, and for the formation of internal threads need straight and curved tools, which are fixed in a special mandrel. The top of the lathe cutter, which is performed by cutting turns, must have a configuration, which fully corresponds to the profile of the molded thread.
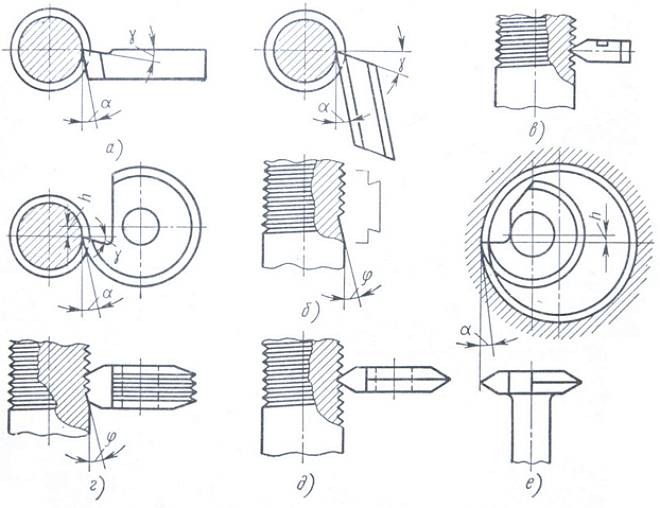
Cutters for threading: and - rod; b - prismatic multidisciplinary; in - prismatic single-profile; g - disk multidisciplinary; d - disk single-profile; e - disk for female thread; ? - rear corner; ? - front corner; ? - angle of the intake cone; h is the installation height of the cutter axis
When forming a thread with a cutter should take into account a number of features of this technology.
- The front angle of the lathe for threading depends on the characteristics of the material, treatable. You can choose such an angle in a fairly wide range: 0-250. So, if the thread is cut with a machine tool on workpieces made of ordinary steels, the front corner should be 0 degrees, for high-alloy steels, which withstand temperature loads well, the front corner may be 5-100. It can be even more so, the higher the viscosity of the material, and even less, the higher the hardness and brittleness of the metal, from which the workpiece is made on the machine.
- The top of the lathe cutter, which forms a twisted line on the workpiece, must have a shape, identical thread profile.
- The rear side corners of the tool are selected as follows, to the surface of the cutter, how they are formed, did not rub against the newly formed twisted groove. Usually these angles on both sides of the lathe are made the same. If the angle of rise, which characterizes the thread, is less 4 degrees, then such angles are chosen within 3-50, if more 40, then 6-8 degrees.
- Internal threads are cut in already prepared holes, which are obtained by boring or drilling.
thread cutters
Blanks, which are made of steel, processed on a lathe using tools with plates, made of hard alloys T15K6, Т14К8, Т15К6, T30K4. If the part is made ??of cast iron, then to cut the thread on it use a tool with plates of the following brands of hard alloys: VK4, V2K, ВК6М, ВК3М.
Technology of use of taps and dies
With the help of taps, representing the screw with several longitudinal grooves, which form cutting edges and promote chip removal, on a lathe cut mainly metric threads in holes of small diameter. If machine taps are used to cut the thread, then the operation is performed in one pass.
Machine taps are different from conventional ones, that they consist of two parts - intake and calibration. If conventional taps are used to cut the thread with a lathe, then the technology of this process involves the use of a set of tools. The set for cutting an internal thread includes three types of taps: rough, which performs 60% work, semi-finished (30%), finishing (10%). Sometimes such a set can have two tools: rough, performing 75% work, and finishing, which accounts for 25% work. To distinguish the rough tap from the finish, just look at its intake: she has it much longer, than the finishing.
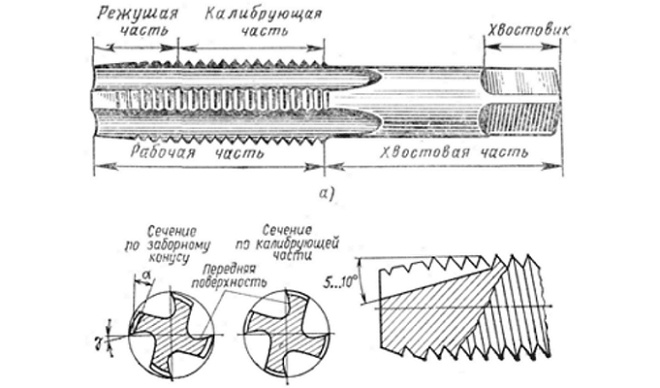
The design of the tap for threading
The speed of threading on a lathe using taps can be quite high:
- 6-22 m per minute - for details, made of cast iron, bronze and aluminum;
- 5-12 m per minute - for steel billets.
With the help of dice, representing a ring with an internal carving and several chip grooves, external carving is done on screws, bolts and studs. The surface of the part must be pre-turned to the required diameter, which must take into account the tolerance:
- 0,14-0,28 mm - for carving, whose diameter is 20-30 mm;
- 0,12-0,24 mm - for threads with a diameter 11-18 mm;
- 0,1-0,2 mm - for carving, having a diameter 6-10 mm.
Dice, which cut the external thread, are fixed in the special cartridge (Riveters), located in the quill of the rear headstock of the lathe.

Dies for carving
Using dice, the threads are cut at the following speeds (their setting also takes into account the minimum wear of the tool during operation):
- 10-15 m per minute - on products, made of brass;
- 2-3 m per minute - on cast iron parts;
- 3-4 m per minute - on steel billets.
That the die freely came to a detail, at the end of the latter remove the chamfer, the height coincides with the height of the thread profile.
The use of cutting heads
When cutting a carving with use of lathes to special heads address much less often, than to the tools described above. Such heads can be used for threading of any type. Their working elements are combs: prismatic are applied, when you need to cut the internal thread, for cutting the outer radial, round and tangential. The peculiarity of such heads is, that their working bodies automatically diverge when reversing, so, they do not come into contact with freshly cut threads.

threaded heads

Combs for carving
Combs for cutting internal threads (their number in the set may be different) are made with a western cone. When cutting the external thread, round combs are mainly used, which differ in simplicity of the design. in addition, This type of comb is characterized by high stability, they can be re-sharpened repeatedly, bringing their geometric parameters to the original values.
In that case, if you need to cut twisted surfaces on worms or screws on a lathe, of great length, then the threaded heads are fixed on the caliper of the machine, which helps to increase the productivity of the technological process. Such heads can be equipped as usual cutters, and a cup-type tool.
It is possible to understand technology of a carving of a carving by means of the lathe on video, on which it is well visible, how this process is carried out. Here are some videos, which depicts the process of making threads in different ways.




