
Alloy of copper with zinc - as it is called, which lead to overheating of the gasoline or diesel engine, marking
Probably many people know, which is brass. And many know, that it is an alloy of copper with zinc, which additionally contains a number of other elements - iron, lead, manganese, nickel and others. However, the key role in this alloy belongs to zinc.

brass wire
Characteristics of copper alloy with zinc content
The alloy of copper with zinc is characterized by the following properties, both corrosion resistance and high strength. The level of corrosion resistance of brass is in the middle of the values of this parameter in copper and the second metal - zinc.
The use of copper-zinc alloy in the manufacture of products of complex shapes, but with its small geometric dimensions it is justified by its technological properties. Such material (as copper and its alloys of another type) well formed, and finished products from it are easily processed by various methods.
Types of brass depending on the zinc content
Brass has a high fluidity and low propensity to liquation, which makes it an ideal material for the production of various parts by casting. in addition, brass is well processed by plastic deformation, which makes it possible to produce from it various products by rolling (wire, ribbons, lists, hire of various profile).
Zinc can be found in brass in quantities 5-45%, alloy on this parameter can belong to different categories. The first category is yellow brass (zinc they contain 20-36%), the second is red (their zinc content is from 5 to 20%). Type of alloy, which is called tompak, contains to 10% zinc. There are brass, zinc in which more 45%, but their use is very limited.
For copper alloys (including zinc) characteristic less heat- and electrical conductivity, if you compare them with the base metal, but their cost is much less. Given this fact, as well as that, which according to the main characteristics - mechanical, technological, as well as antifriction - such materials differ little from the base metal, it is economically more expedient to use them.

Brass cylinder
Brass, consisting of two or more components
Among the alloys of copper with zinc are not only red and yellow, but also two-, as well as multicomponent brass. The composition of two-component alloys includes mainly copper and zinc, there are very few other inclusions in them. Here, in particular, refers to tompak, zinc in which, as noted above, contains no more 10%. The amount of copper in this alloy can reach 97%, and its minimum content is 88%.
Two-component brass can be the same- and two-phase. In single-phase, characterized by high plasticity, zinc is present in a solid solution. If we compare single-phase and two-phase brass, the second is less plastic, but have greater strength, zinc in such alloys contains more 39%.
As single-phase, and two-phase brass can be deformed at high temperatures (300-700 degrees Celsius). Under such conditions, a zone of fragility is formed in them.
In the structure of an alloy of copper with zinc, belonging to the category of multicomponent, there are additional alloying elements. Let's list them.
- Nickel increases the corrosion resistance of the alloy, as well as its strength.
- Tin not only increases strength, but also the resistance of the alloy to salt water.
- Silicon alloy is enriched for this purpose, to improve the antifriction characteristics of its products. However, this element degrades the strength, as well as the hardness of alloys.
- Lead when added to the alloy significantly improves the machinability of its products with cutting tools. Meanwhile, lead degrades the mechanical properties of the metal.
- Manganese, as well as tin, improves the strength and corrosion resistance of alloys. Usually, along with manganese tin is added to brass, iron and aluminum, which significantly increases the effect of using this alloying element.
- Combining alloying elements, added to brass, it is possible to obtain copper alloys with the required qualitative and technological characteristics, as well as give them special properties, if necessary.
Marking of alloys, consisting of copper and zinc
Marking of copper alloys, which contain zinc, based on a fairly simple principle. In the designation of any alloy of copper with zinc (as two, and multicomponent) there is a letter "L", which is the first. In two-component alloys, this letter is followed by numbers, denoting the copper content in whole percentages. So, by this figure you can immediately find out, what percentage of copper is contained in this brand of brass.
Multicomponent brass differs in more difficult marking, in the designation of which there are several letters and numbers. The first letter is "L", which makes it clear, that in front of us is brass, this letter is followed by letter designations of various alloying elements. The second part of the labeling of multicomponent alloys is the percentage of alloying elements, specified in the letter part of the label. For greater convenience figures, which correspond to the content of each alloying element, separated by hyphens. The order of numbers in the labeling of multicomponent brass is as follows:
- the first two digits are the copper content;
- other figures, separated by hyphens, correspond to the content of alloying elements, specified in the letter part of the label.

Brass Marking Guide
To make it clearer, let's disassemble, what elements are contained in the alloy of copper with zinc brand LAZHMts66-6-3-2. According to the first digit, this alloy contains 66% copper, followed by Aluminum (6%), Iron (3%) and Manganese (2%). If we sum up these figures, it can be determined, that copper with other elements in this brass is contained 77%. Rest 23% is zinc.
Brass is marked in a slightly different way, belonging to the category of foundries. In their markings immediately after the letters, denoting alloying elements, put numbers, corresponding to their percentage. Example, in the alloy of the LC40Mts1,5 brand contains:
- 40% zinc;
- 1,5% manganese;
- remained 58,5% is copper.

brass bushings
Brass, belonging to the category of deformable and cast alloys
Brass, belonging to the category of alloys, deformable, differ in the increased resistance to corrosion, they are very ductile and have exceptional antifriction characteristics. Copper-zinc alloys of this category are well welded with steel products. This property makes it possible to use them for the production of various bimetallic structures. Yellow brass has an attractive appearance, due to which it is often used for the production of various accessories and decorative products.
Brass, belonging to the category of alloys, deformable, used for production:
- condenser tubes (for these purposes brass of the LMsh68-0,05 brands is required, LO60-1, LO62-1, LO70-1, LO90-1, LA77-2);
- which have increased corrosion resistance of machine parts, river, ships (L68 brass is used here, L80, L90);
- details, which are made by a method of cutting (LZhS58-1-1 brass is used for production of such details);
- different bushings, fasteners - bolts, nuts, etc.. (For the production of such products brass brands LS59-1 are used, LMc58-2, LS60-1);
- matrices, used in the printing industry (for such products brass of the LS64-2 brand is required).
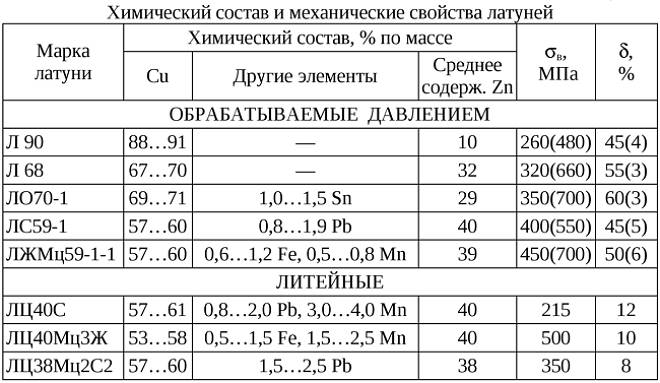
Composition and properties of different types of brass
Brass, belonging to the category of foundry alloys, used for the production of such products, as:
- fittings, which are used to equip hydraulic systems of cars (ЛЦ25С2);
- bearings and separators of various types (LC40S);
- worm-type screws, have large dimensions and weight (ЛЦ23А6Ж3Мц2);
- parts with special properties, which are operated at temperatures, exceeding 300 degrees Celsius (LTs40Mts3Zh);
- details, which are subject to increased requirements for corrosion resistance (LC30A3).




