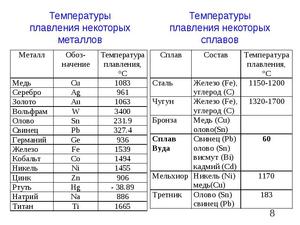
Table of melting temperatures of different metals, and at what degrees they melt
Each metal and alloy has its own unique set of physical and chemical properties, among which the melting temperature takes not the last place. The process itself means the transition of the body from one state to another, in this case, from solid crystalline state to liquid. To melt metal, it is necessary to bring heat to it before reaching the melting point. With it, he can still remain in a solid state, but with further exposure and increased heat, the metal begins to melt. If the temperature is lowered, that is, remove some of the heat, the element hardens.

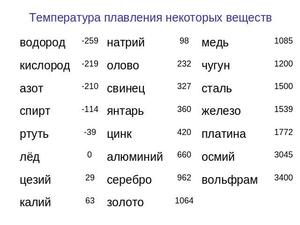
The highest melting point among metals belongs to tungsten: it is 3422Co, the lowest is in mercury: the element melts at 39Co. Determine the exact value for alloys, usually, does not represent a possibility: it can vary considerably depending on the percentage of components. They are usually written as a numerical interval.
How it happens
Melting of all metals is approximately the same - by external or internal heating. The first is carried out in a thermal furnace, for the second use resistive heating when passing an electric current or induction heating in a high-frequency electromagnetic field. Both options affect the metal approximately equally.
As the temperature increases, the amplitude of thermal oscillations of molecules also increases, there are structural defects of the lattice, expressed in the growth of dislocations, jumping atoms and other violations. This is accompanied by the rupture of interatomic bonds and requires a certain amount of energy. At the same time, a quasi-liquid layer is formed on the surface of the body. The period of destruction of the lattice and the accumulation of defects is called melting.
Separation of metals
Depending on the melting point of metals are divided into:
Fusible: they need no more than 600Co. This is zinc, lead, hang, lead.
- Medium melting: melting point ranges from 600Co to 1600Co. Is this gold, copper, aluminum, magnesium, iron, nickel and more than half of all elements.
- Refractory: required temperature above 1600Co, to make the metal liquid. Chromium belongs here, tungsten, molybdenum, titanium.
Depending on the melting temperature and choose the melting device. The higher the figure, the stronger it should be. You can find out the temperature of the element you need from the table.
Another important value is the boiling point. This is a quantity, at which the process of boiling liquids begins, it corresponds to the temperature of saturated steam, formed above the flat surface of the boiling liquid. Usually it is almost twice as much, than the melting point.
Both values are usually given at normal pressure. They are directly proportional to each other.
- The pressure increases - the amount of melting will increase.
- Pressure decreases - the amount of melting decreases.
Table of refractory metals and alloys (up to 600C about )
| Item name | Latin designation | Temperatures | |
| Melting | Boiling | ||
| Lead | Sn | 232 WITH | 2600 From |
| Lead | Pb | 327 WITH | WITH 1750 |
| Zinc | Zn | 420 WITH | WITH 907 |
| Potassium | K | 63,6 WITH | 759 From |
| Sodium | On | 97,8 WITH | 883 WITH |
| Mercury | Hg | - З 38,9 | 356.73 WITH |
| Cesium | Cs | 28,4 WITH | 667.5 WITH |
| Bismuth | With a | 271,4 WITH | WITH 1564 |
| Palladium | Pd | 327,5 WITH | WITH 1749 |
| Polonium | Po | 254 WITH | 962 WITH |
| Cadmium | Cd | 321,07 WITH | 767 WITH |
| Rubidium | Rb | 39,3 WITH | 688 WITH |
| Gallium | Ga | 29,76 WITH | 2204 WITH |
| India | In | 156,6 WITH | 2072 WITH |
| Thallium | Tl | 304 WITH | WITH 1473 |
| Lithium | At the | 18,05 WITH | 1342 WITH |
Table of medium-melting metals and alloys (from 600C to 1600C )
| Item name | Latin designation | Temperatures | |
| Melting | Boiling | ||
| Aluminum | Al | 660 WITH | 2519 WITH |
| Germanium | Give | 937 WITH | 2830 WITH |
| Magnesium | Mg | 650 From | 1100 From |
| Silver | Ag | 960 From | 2180 WITH |
| Gold | At | 1063 WITH | 2660 WITH |
| Copper | With | 1083 From | 2580 WITH |
| Iron | Fe | WITH 1539 | 2900 From |
| Silicon | And | WITH 1415 | 2350 WITH |
| Nickel | Ni | 1455 WITH | 2913 WITH |
| Barium | Ba | 727 WITH | WITH 1897 |
| Beryllium | Be | 1287 WITH | 2471 WITH |
| Neptunium | E.g | 644 From | 3901,85 WITH |
| Protactin | Well | WITH 1572 | 4027 WITH |
| Plutonium | Could | 640 WITH | 3228 WITH |
| Actinium | Ac | 1051 From | 3198 WITH |
| Calcium | That | 842 WITH | 1484 WITH |
| Radium | Out | 700 From | 1736,85 WITH |
| Cobalt | Co | WITH 1495 | 2927 WITH |
| Trumpet | Sb | 630,63 WITH | WITH 1587 |
| Strontium | Sr | 777 WITH | 1382 WITH |
| Uranium | U | 1135 WITH | 4131 WITH |
| Manganese | Mn | 1246 WITH | From 2061 |
| Constantine | WITH 1260 | ||
| Duralumin | Aluminum alloy, magnesium, copper and manganese | 650 From | |
| Invar | Alloy of nickel and iron | WITH 1425 | |
| Brass | Alloy of copper and zinc | 1000 From | |
| Neisilber | Copper alloy, zinc and nickel | 1100 From | |
| Nichrome | Nickel alloy, chromium, silicon, iron, manganese and aluminum | WITH 1400 | |
| Steel | Alloy of iron and carbon | 1300 C - 1500 From | |
| Fehral | Chromium alloy, iron, aluminum, manganese and silicon | WITH 1460 | |
| Cast iron | Alloy of iron and carbon | 1100 C - 1300 From | |
Table of refractory metals and alloys (over 1600C Fr. )
| Item name | Latin designation | Temperatures | |
| Melting | Boiling | ||
| Tungsten | W | 3420 WITH | 5555 WITH |
| Titanium | You | WITH 1680 | 3300 From |
| Iridium | Ir | 2447 WITH | 4428 WITH |
| Osmium | You | 3054 WITH | 5012 WITH |
| Platinum | Pt | 1769,3 WITH | 3825 WITH |
| Rhenium | Re | 3186 WITH | 5596 WITH |
| Chromium | Cr | 1907 From | 2671 WITH |
| Rhodium | Rh | WITH 1964 | 3695 WITH |
| Ruthenium | Ru | 2334 WITH | 4150 WITH |
| Hafnium | Hf | 2233 WITH | 4603 WITH |
| Tantalum | Ta | 3017 WITH | 5458 WITH |
| Technetium | Tc | 2157 WITH | 4265 WITH |
| Thorium | Th | WITH 1750 | 4788 WITH |
| Vanadium | V | WITH 1910 | 3407 WITH |
| Zirconium | Zr | WITH 1855 | 4409 WITH |
| Niobium | Nb | 2477 WITH | 4744 WITH |
| Molybdenum | Mo | 2623 WITH | WITH 4639 |
| Hafnium carbides | 3890 WITH | ||
| Niobium carbides | 3760 WITH | ||
| Titanium carbides | 3150 WITH | ||
| Zirconium carbides | 3530 WITH | ||




