
Copper melting point - at what temperature copper melts
Thanks to that, that the melting point of copper is quite low, this metal was one of the first, which ancient people began to use to make various tools, utensils, jewelry and weapons. Nuggets of copper or copper ore could be melted by fire, what, actually, and did our distant ancestors.

Stage of melting copper
Despite the active use by mankind since ancient times, copper is not the most common natural metal. In this respect, it is much inferior to other elements and ranks only 23rd among them.
How our ancestors smelted copper
Due to the low melting point of copper, component 1083 degrees Celsius, our distant ancestors not only successfully extracted pure metal from ore, but also made various alloys based on it. To obtain such alloys, copper was heated and brought to a liquid molten state. Then tin was simply added to this melt or reduced on the surface of molten copper, for which tin-containing ore was used (cassiterite). This technology was used to obtain bronze - an alloy, having high strength, which was used to make weapons.
What processes occur during the melting of copper
What is characteristic, melting point of copper and alloys, obtained on its basis, differ. When adding tin to copper, has a lower melting point, get bronze with a melting point 930-1140 degrees Celsius. And an alloy of copper with zinc (brass) melt at 900-10500 Celsius.
The same processes take place in all metals during the melting process. Upon receipt of sufficient heat when heated, the crystal lattice of the metal begins to break down. At that moment, when it goes into a molten state, its temperature does not rise, although the process of heat transfer by heating does not stop. The temperature of the metal begins to rise again only then, when it all goes into a molten state.
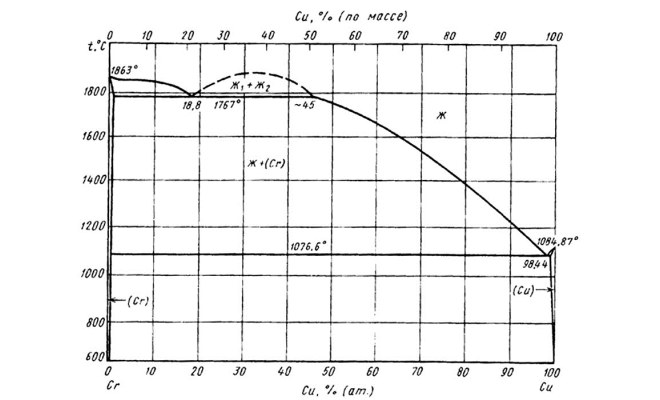
State diagram of the chromium-copper system
When cooling, the opposite process occurs: at first the temperature drops sharply, then stops at a permanent mark for a while. After, as all the metal goes into solid phase, the temperature begins to decrease again until it cools completely.
Like melting, and reverse crystallization of copper, related to the specific heat parameter. This parameter characterizes the specific amount of heat, which is needed for that, to convert metal from solid to liquid. During metal crystallization, this parameter characterizes the amount of heat, which he gives when cooled.
The phase diagram helps to learn more about copper melting, showing the dependence of the state of the metal on temperature. Such diagrams, which can be folded for any metals, help to study their properties, determine the temperature, in which they radically change their properties and current state.
In addition to the melting point, copper has the boiling point at which the molten metal begins to emit bubbles, filled with gas. In fact, no boiling of copper occurs, it's just that this process looks very much like him. It can be brought to such a state, if heated to temperature 2560 degrees.
As is clear from all the above, it is the low melting point of copper can be called one of the main reasons, that today we can use this metal, which has many unique characteristics.




