
Thermal conductivity of copper and its alloys - pros and cons
High thermal conductivity of copper and other useful characteristics have become one of the reasons for the early development of this metal by man. To this day, copper and copper alloys are used in almost all areas of our lives.

Copper plates
A little about thermal conductivity
Thermal conductivity is understood by physicists as the movement of energy in an object from the warmest tiny particles to the least heated. Due to this process the temperature of the considered subject as a whole is equalized. The magnitude of the ability to conduct heat is characterized by the coefficient of thermal conductivity. This parameter is equal to the amount of heat, which passes through a thick material 1 meter across the surface area 1 m2 for one second at a single temperature difference.
Material Coefficient of thermal conductivity, W /(m * K)
| Silver | Four hundred and twenty-eight |
| Copper | Three hundred and ninety-four |
| Aluminum | Two hundred and twenty |
| Iron | Seventy-four |
| Steel | Forty-five |
| Lead | Thirty-five |
| Brick | 0,77 |
Copper has a coefficient of thermal conductivity 394 W /(m * K) at a temperature of 20 to 100 ° C. Only silver can compete with it. And in steel and iron this figure is lower than 9 and 6 times respectively (div. table). It is worth noting, that the thermal conductivity of products, made of copper, largely depends on impurities (however, this also applies to other metals). Example, the rate of heat conduction decreases, if such substances get into copper, as:
- iron;
- arsenic;
- oxygen;
- selenium;
- aluminum;
- trumpet;
- phosphorus;
- sulfur.

Copper wire
If you add zinc to copper, then brass will come out, in which the thermal conductivity is much lower. At the same time, the addition of other substances, copper can significantly reduce the cost of finished products and give them the following characteristics, as strength and durability. Example, brass is characterized by higher technological, mechanical and antifriction properties.
Because high thermal conductivity is characterized by rapid spread of heating energy throughout the object, copper has been widely used in heat exchange systems. At the moment, radiators and tubes for refrigerators are made of it, vacuum installations and cars for fast removal of heat. Copper elements are also used in heating systems, but already for heating.

Copper heating radiator
To maintain the thermal conductivity of the metal at a high level (so, make the operation of copper devices as efficient as possible), in all heat exchange systems use forced blowing by fans. This decision is due to that, that with increasing ambient temperature, the thermal conductivity of any material is significantly reduced, after all, heat transfer is slowed down.
Aluminum and copper are better?
Aluminum has one disadvantage compared to copper: its thermal conductivity in 1,5 times less, namely 201-235 W /(m * K). However, compared to other metals, this is quite high. Aluminum is the same, as well as copper, has high anti-corrosion properties. in addition, it has the following advantages, as:
- low density (specific weight in 3 times less, than in copper);
- low cost (in 3,5 times less, than in copper).

Aluminum heating radiator
Thanks to simple calculations it turns out, that aluminum part can be cheaper than copper in 10 times, because it weighs much less and is made of cheaper material. This fact, along with high thermal conductivity allows the use of aluminum as a material for dishes and food foil for ovens. The main disadvantage of aluminum is, that it is softer, therefore, it can be used only in alloys (example, duralumin).
The rate of heat transfer to the environment plays an important role in efficient heat exchange, and this is actively facilitated by the cooling of radiators. As a result, lower thermal conductivity of aluminum (regarding copper) leveled, and the weight and cost of equipment are reduced. These important advantages allow aluminum to gradually displace copper from use in air conditioning systems.

The use of copper in electronics
In some areas, example, in the radio industry and electronics, copper is indispensable. The point is, that this metal is by nature very malleable: it can be pulled with extremely thin wire (0,005 mm), and create other specific conductive elements for electronic devices. And high thermal conductivity allows copper to remove extremely effectively heat which inevitably arises at work of electric devices., which is very important for modern high-precision, but at the same time compact technology.
It is important to use copper in those cases, when it is necessary to make surfacing of a certain form on a steel detail. A copper template is used, which does not connect to the welded element. It is impossible to use aluminum for these purposes, as it will be melted or scorched. It is also worth mentioning, that copper is able to act as a cathode in carbon arc welding.
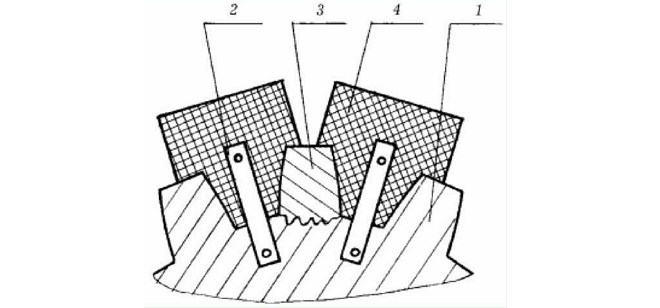
1 - gear, 2 - fastening templates, 3 - the gear tooth is welded, 4 - copper templates
Disadvantages of high thermal conductivity of copper and its alloys
Copper has a much higher cost, than brass or aluminum. However, this metal has its drawbacks, directly related to its merits. High thermal conductivity leads to the need to create special conditions during cutting, welding and soldering of copper elements. As it is necessary to heat copper elements much more concentrated in comparison with steel. Pre-heating and associated heating of the part are also often required.
We should not forget about that, that copper pipes require careful insulation in that case, if they consist of a mains or heating system. Which leads to an increase in the cost of installing the network compared to the options, when other materials are used.

An example of thermal insulation of copper pipes
Difficulties also arise with gas welding of copper: this process requires more powerful burners. When welding thick metal 8-10 mm requires two or three burners. While one burner is used for welding, others are heating parts. In general, welding work with copper requires increased costs for consumables.
It should be said about the need to use special tools. So, for cutting brass and bronze up to 15 see you will need a cutter, able to work with high-chromium steel with a thickness of 30 div. And the same tool will suffice for work with pure copper only in thickness 5 div.

Plasma cutting of copper
You can increase the thermal conductivity of copper?
Copper is widely used in the creation of chips of electronic devices and is designed to dissipate heat from electrically heated parts. In an attempt to increase the speed of modern computers, developers have faced the problem of cooling processors and other parts. As one of the solutions used the option of splitting the processor into several cores. However, this method of combating overheating has exhausted itself, and now we need to look for new conductors with higher thermal and electrical conductivity.
One solution to this problem is the recently discovered element graphene. Due to the graphene coating, the thermal conductivity of the copper element increases by 25%. However, so far the invention is at the development level.




