
Metal turning - technology, specifics, video
The most common methods of manufacturing parts with specified geometric parameters include metal turning. The essence of this technique, which also allows you to get a surface with the required roughness, is, that the extra layer of metal is removed from the workpiece.

The process of turning metal
Principles of turning
The technology of turning work on metal involves the use of special machines and cutting tools (cutters, drills, sweeps, etc.), by means of which a layer of metal of the required size is removed from the part. Turning is performed by combining two movements: the main thing (rotation of the workpiece, fixed in the cartridge or faceplate) and feed motion, performed by the tool when processing parts to the specified parameters of their size, surface shape and quality.
Due to that, that there are many ways to combine these movements, on the turning equipment work with details of various configuration, and also carry out the whole list of other technological operations, to which they belong:
- threading of various types;
- drilling holes, their boring, deployment, countersinking;
- cutting off part of the workpiece;
- drilling on the surface of the product grooves of different configurations.
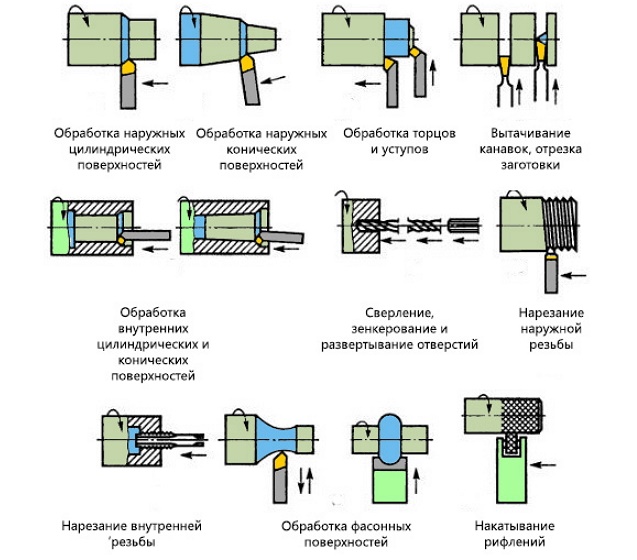
The main types of turning work on metal
Thanks to such a wide functionality of turning equipment, a lot can be done on it. Example, with its help carry out processing of such products, as:
- nuts;
- shafts of different configurations;
- bushings;
- pulleys;
- rings;
- couplings;
- gears.
Naturally, that turning involves obtaining a finished product, which meets certain quality standards. Quality in this case means compliance with the requirements for geometric dimensions and shapes of parts, as well as the degree of surface roughness and the accuracy of their relative position.
Measuring instruments are used to ensure control over the quality of processing on lathes: at enterprises, producing their products in large series, - limit calibers; for conditions of single and small-scale production - calipers, micrometers, nutrometers and other measuring devices.

Measuring instruments, which are often used in turning
First, considered in the training of turning, Is a technology of metal processing and a principle, by which it is carried out. This principle is, that tool, crashing its cutting edge into the surface of the product, clamps. To remove a layer of metal, which corresponds to the magnitude of such an incision, the tool must overcome the forces of adhesion in the metal of the workpiece. As a result of such interaction the removed layer of metal is formed in shaving. There are the following types of metal shavings.
Merged
Such shavings are formed then, when workpieces are processed at high speeds, made of mild steel, copper, tin, lead and their alloys, polymeric materials.
Elementary
The formation of such shavings occurs, when low-viscosity and hard materials are processed at low speeds.
Broken shavings
Chips of this type are obtained when processing workpieces from the material, has low ductility.
Step by step
The formation of such chips is typical for medium-speed processing of steel workpieces of medium hardness, parts of aluminum alloys.
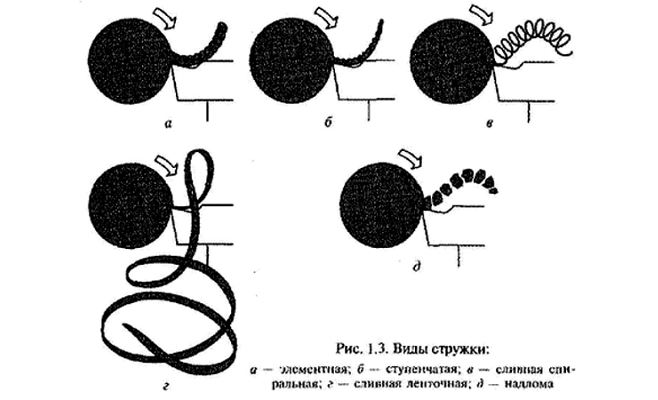
Types of shavings in turning
Lathe cutting tool
Efficiency, how different is the work on the lathe, determined by a number of parameters: depth and speed of cutting, the amount of longitudinal feed. That finishing of a detail was high-quality, it is necessary to organize such conditions:
- high speed of rotation of the workpiece, which is fixed in the cartridge or faceplate;
- the stability of the tool and the sufficient degree of its impact on the part;
- the maximum possible layer of metal, which is removed for the passage of the tool;
- high stability of all units of the machine and maintaining them in working order.
The cutting speed is selected based on the characteristics of the material, from which the workpiece is made, type and quality of the cutter used. In accordance with the selected cutting speed, the speed of the machine spindle is selected, equipped with a turning chuck or faceplate.
With the help of different types of cutters you can perform roughing or finishing types of turning work, and the choice of tool is mainly influenced by the nature of processing. Changing the geometric parameters of the cutting part of the tool, you can adjust the size of the layer, removable metal. There are right cutters, which in the process of processing the parts move from the rear headstock to the front, and left, moving, in accordance, in the opposite direction.
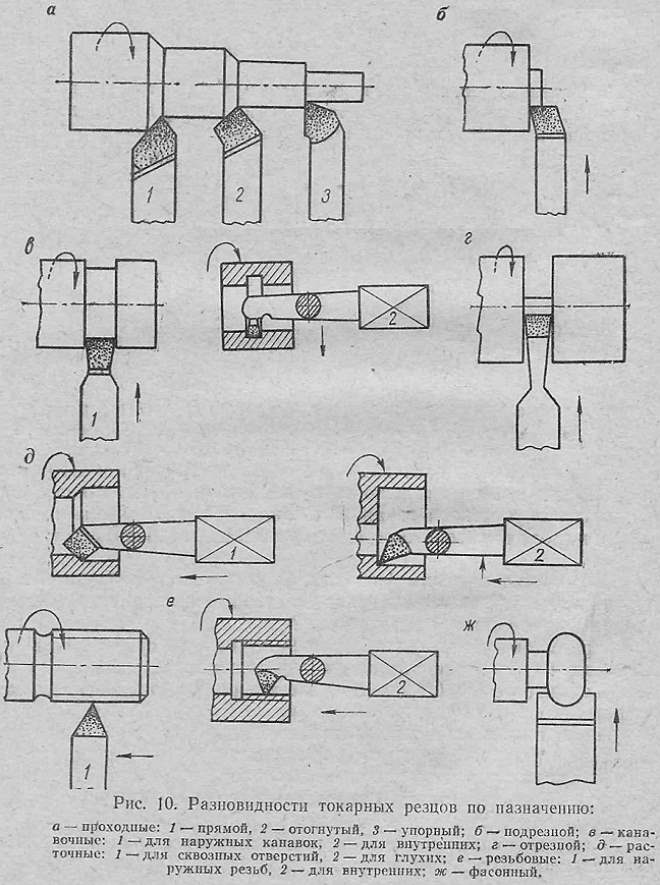
The main types of turning cutters
The shape and location of the blades cutters are classified as follows:
- tools with extended working part, the width of which is not less than the width of their fasteners;
- direct;
- bent.
There are cutters and the purpose of application:
- undercut (surface treatment, perpendicular to the axis of rotation);
- checkpoints (turning of flat end surfaces);
- grooving (formation of grooves);
- shaped (obtaining a part with a specific profile);
- boring (boring holes in the workpiece);
- threaded (threading of any kind);
- detachable (cutting a part of a given length).
Quality, accuracy and productivity of processing, performed on a lathe, depend not only on the right choice of tool, but also from its geometric parameters. That is why in lessons in special schools, where future turning specialists study, very much attention is paid to the geometry of the cutting tool.
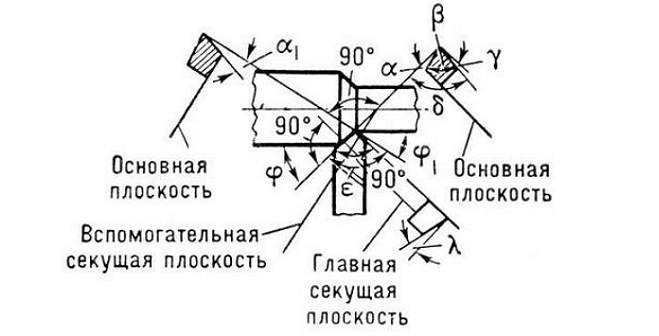
Angles of a turning cutter
The main geometric parameters of any cutter are the angles between the cutting edges and the direction, in which the supply is made. Such angles of the cutting tool are called angles in the plan. Among them are distinguished:
- main corner - ?, measured between the main cutting edge of the tool and the feed direction;
- auxiliary - ?1, situated, in accordance, between the auxiliary edge and the feed direction;
- angle at the top of the cutter - ?.
The angle at the top depends only on that, as a sharpened tool, and auxiliary corners can be adjusted also by its installation. As the main angle increases, the angle at the apex decreases, at the same time the part of a cutting edge decreases also, involved in processing, in accordance, the stability of the tool also becomes less. The smaller the value of this angle, the greater part of the cutting edge is involved in both processing, and in the removal of heat from the cutting zone. Such cutters are more stable.
Practice shows, that the main angle is optimal for turning not too rigid workpieces of small diameter, the value of which is in the range 60-90 degrees. If it is necessary to process a workpiece of large diameter, then the main angle must be selected in the interval 30-45 degrees. The strength of the cutter tip depends on the strength of the auxiliary angle, so they don't make it big (usually, it is selected from the interval 10-30 degrees).
Particular attention is paid to turning in the lessons in turning, how to choose the right type of cutter depending on the type of processing. So, there are certain rules, according to which the treatment of surfaces of one type or another is performed using a cutter of a certain category.
- Conventional straight and curved cutters are needed to finish the outer surfaces of the part.
- Pass-through stop tool is required for end and cylindrical surfaces.
- The cutting cutter is chosen for drilling grooves and trimming the workpiece.
- Boring cutters are used for machining holes, drilled before.
A separate category of turning tools are cutters, by means of which it is possible to process shaped surfaces with length of a generating line to 40 mm. Such cutters are divided into several main types:
- on design features: rod, round and prismatic;
- in the direction, in which the product is processed: radial and tangential.

Screw-cutting lathe 1B625MP
Types of equipment for turning
Of all the types of turning equipment, the most common are large ones, and at small enterprises received a lathe. The reason for this popularity is the versatility of this device, thanks to which it can rightly be called universal.
List the main elements of the design of such a machine:
- two grandmothers - front and back (in the front headstock place the gearbox of the machine; spindle with lathe chuck (or faceplate), longitudinal sledges and quill equipment are placed on the rear headstock);
- carriage, in the design of which there are upper and lower sledges, rotary plate and tool holder;
- the load-bearing element of the equipment is a frame, mounted on two pedestals, in which electric motors are placed.
- gearbox.

CNC lathe
Machines are becoming more common, which are controlled by special computer programs CNC machines. The design of such machines differs from the usual only in that, that there is a special control unit.
The following types of lathes are divided into separate categories:
- turning and turret equipment, used for machining parts of complex configuration;
- rotary lathes, among which there are one - and two-rack;
- multi-cutter semi-automatic equipment, which can be found in enterprises, producing their products in large series;
- processing complexes, on which it is possible to carry out as lathes, and milling operations.
Without turning today, it is extremely difficult to imagine many industries. Therefore, this type of work with metal continues to develop, despite the already high level, that allows to provide the highest quality and speed of processing.




