
Carbon tool steels: see, application, GUEST
Specifications, which are different carbon tool steels, allow you to successfully use this material not only for the manufacture of tools for various purposes, but also for the production of molds for casting, measuring instruments, as well as other products, the accuracy of the geometric parameters of which are subject to increased requirements.

The properties of carbon steels allow them to be used in the manufacture of molds for high-precision casting
The main features
The modern metallurgical industry produces steel in significant quantities, as it is one of the main construction materials. Part of the steel, the composition of which is enriched with alloyed elements, which is in this amount only 10%, the other part is structures and products made of ordinary carbon alloys. This fact indicates, that carbon steel can be called the main material, used in modern industry.

Carbon steel products surround us everywhere
The prevalence of carbon steel is explained:
- low cost of production;
- good workability by various methods (cutting, pressure, welding);
- good performance data.
Tool steels, relating to alloys of the carbon group, which distinguishes a complex chemical composition, the basis of which (97-99,5%) is iron. Except for the latter, they contain the following elements:
- chromium, nickel and copper (they are added specially);
- sulfur, phosphorus, nitrogen, oxygen, hydrogen (these elements are present in the tool steel back, that they are completely impossible to remove when cleaning it);
- manganese and silicon (their appearance is determined by the peculiarities of the production of carbon tool steels).
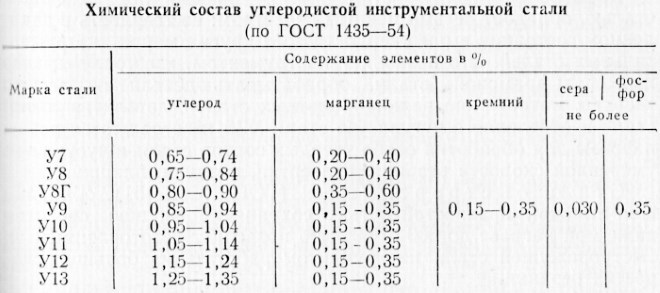
The content of basic chemical elements in carbon steel
Carbon has a significant effect on the characteristics of tool steels, which is deliberately introduced into their composition. Modification of the alloy structure depends on the amount of this element. So, in tool steels, containing less than eight tenths of a percent of carbon, pearlitic and ferritic internal structure, more than eight tenths of a percent - cementite and pearlitic, exactly eight tenths of a percent - completely pearlitic.
The large amount of carbon in the composition of carbon tool steels determines the following characteristics:
- low ductility and good toughness;
- extremely high strength;
- resistance to cold machining.
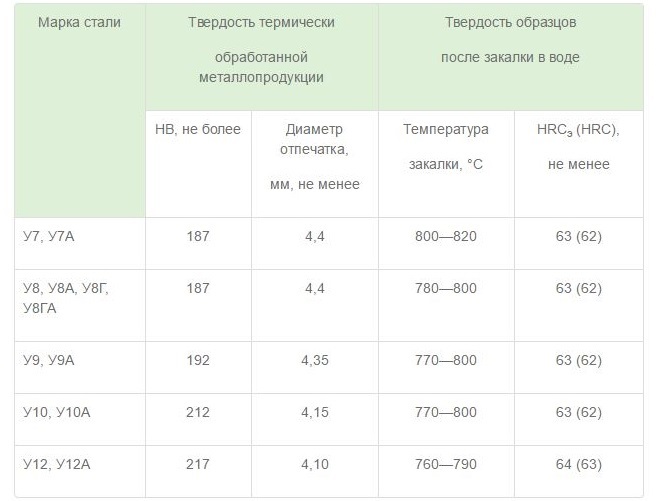
Hardness of metal products from carbon steels
On the characteristics of alloys, which contain a significant amount of carbon, iron oxides have a negative effect. To reduce this impact, the following elements are specially introduced into the composition of carbon steels:
- silicon (part of the volume of this element is converted into the form of silicate inclusions, the rest of its amount is completely soluble in ferrite);
- manganese (used for deoxidation of iron-carbon alloy, but at the same time solves other important tasks: removal from ferrite and cementite, forming the basis of the alloy, iron compounds with sulfur, which have an extremely negative impact on its quality; increase the strength of metal sheets, obtained from hot-rolled technology).
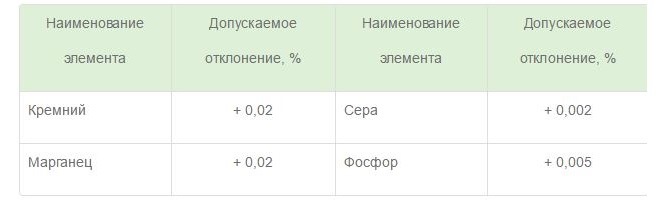
Permissible deviations in chemical composition in rolled products, intended for further processing
Production methods
The most efficient and economical way to produce carbon tool steels, which has been used for many years, there is an oxygen-converter technology. It consists in purging liquid cast iron, poured into the converter, oxygen. The duration of the production process for this technology does not exceed one hour. Carbon steels are also smelted in open-hearth and electric furnaces, Bessemer-type converters are used for this purpose.

Carbon steel smelting
Production of carbon tool steels in Bessemer-type converters is characterized by high productivity, but has a number of significant disadvantages. When using this technology from the finished alloy can not remove all impurities of non-metallic nature. Such steel contains a significant amount of nitrogen and other gaseous inclusions, which reduce its density and strength, lead to rapid aging of the metal. In the so-called Bessemer steels, in addition, contains a lot of phosphorus and sulfur, remove which is not entirely possible.
Oxygen-converter method allows to remove phosphorus and sulfur or bring their content in metal to an acceptable level. Steel, obtained by this technology, also have a low content of nitrogen and other gaseous inclusions. Smelting of carbon tool steels in open-hearth furnaces allows to obtain similar characteristics, but this technology has one major drawback - the duration of implementation. To smelt steel in such a furnace, it is necessary approximately 11 hours, which negatively affects the economic feasibility of this process.
Get the highest quality tool steel, which contains a minimum amount of phosphorus, sulfur and oxygen, technology allows, involving the use of arc or induction electric furnaces.

Compact Lego induction melting furnaces are housed in small production facilities
This technology (the most expensive of all) allows you to receive materials, which are designed for the manufacture of responsible metal structures. Due to the high cost of this method, many metallurgical enterprises do not use it, preferring more economical technologies.
Classification
Carbon steels, belonging to different categories, it is accepted to divide on quality level into the following types:
- metal of the highest quality, in which there is no more 0,03% sulfur and phosphorus;
- quality steel, which are characterized by such a content of harmful impurities: phosphorus - no more 0,035%, sulfur - no more 0,04%;
- steel of ordinary quality, which contains no more 0,05% sulfur and no more 0,04% phosphorus.
Steel alloys, which belong to the category of instrumental, can only be high quality and high quality. Requirements for structural steels are slightly lower, in this category may be alloys of ordinary quality and quality.
The amount of carbon in the steel alloy also has an effect, to which category it belongs. So, steel with a carbon content does not exceed 0,25%, belong to the category of low-carbon, Rivne 0,6% contain medium carbon, more 0,6% - high carbon.

Diagram of the microstructure of carbon steel depending on the carbon content (dark field - perlite, light - ferrite)
The type of structure of carbon steels may also differ. Depending on it, such alloys are divided into the following categories:
- pre-eutectoid;
- eutectoid;
- eutectoid.
Application and labeling
Alloys of instrumental type include alloys, in which carbon is contained in the range of 0.65-1.35%. Their chemical composition, as well as characteristics, to which they must correspond, determined by the provisions of GOST 1435-74 (is edited by 1999 year).
It is possible to get acquainted with all requirements of GOST to tool steels, by downloading this document in pdf format at the link below.
GUEST 1435-74 Non-alloy tool steel. Specifications
Download
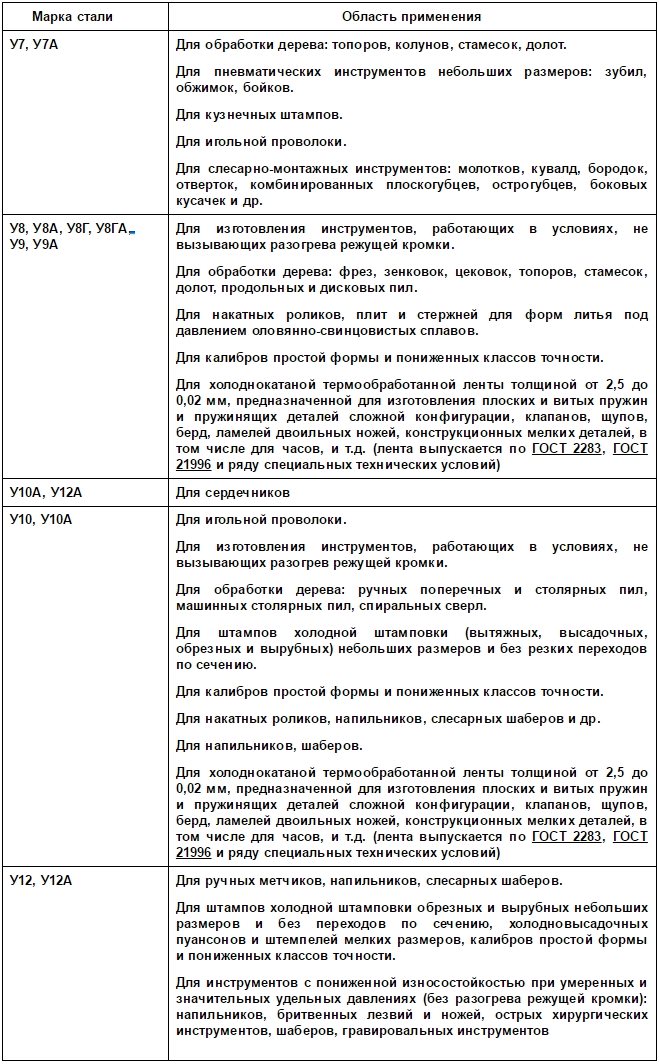
Areas of application of carbon tool steels
The use of carbon tool steels is associated with production:
- incisors, hacksaw blades, files, measuring instrument (brands U11-U13A);
- pneumatic tool, chisels, nippers of different types, trade winds, hammers (U7 and U7A);
- taps, die, scan, drill, matrices for cold stamping (U9-U10A);
- punson, countersinking tools, milling and woodworking, knives, stamps (U8 and U8A).
You can learn more about the marking of carbon tool steels, how much carbon is in their composition, but also about quality categories, to which they belong. So, designation U8A, example, talk about it, that in this alloy, which is of high quality, contained 0,8% carbon.

Examples of designation of rolled carbon steel
When using carbon tool steels should be borne in mind, that products from them are subject to obligatory annealing, tempering and subsequent leave. These types of heat treatment, carried out at the appropriate temperature, allow to optimize the structure of such alloys and, in accordance, significantly improve their hardness and strength.




