
Carbon structural steels: application and labeling
Carbon structural steels can rightly be called a universal material, which is successfully used not only for the production of parts of various machines and mechanisms, but also for the manufacture of structural elements. The possibility of such a wide use of this material is provided by a set of quality characteristics, which he owns.

Structural steel grade 14 G2AF (square) designed for the manufacture of responsible products
What is structural steel
This category includes carbon steels, which must have a set of technological characteristics, determining the effective and long-term operation of their products. This is possible due to that, that specialists carefully select the chemical composition of alloys, constantly improving methods of strengthening their surface layer, use different heat treatment technologies, as well as metallurgical methods, that can significantly improve the quality of the finished metal.
By purpose, structural steels are divided into two types:
- alloys for production in the machine-building sphere;
- construction structural steels, which are also called reinforcing (they are distinguished by good weldability).
Carbon steels, which are called structural, can be general or special purpose. In their chemical composition, in addition to useful additives, containing harmful impurities, the most significant of which are sulfur and phosphorus. The high content of these elements in the steel makes its products very fragile, and also significantly impairs their weldability.
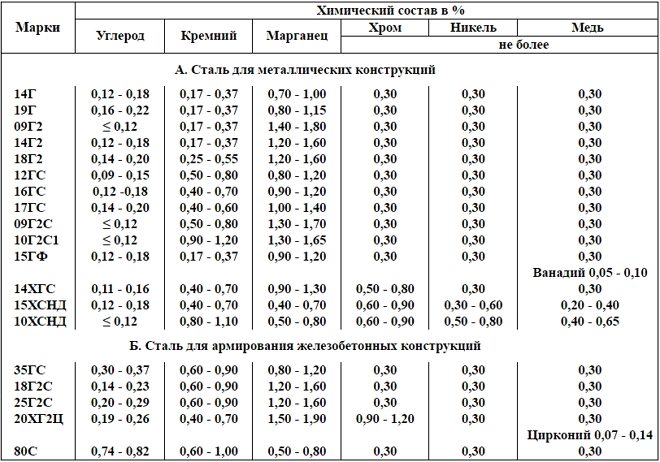
Chemical composition of carbon structural steels
It is because of the serious effects of such harmful impurities, both sulfur and phosphorus, on the characteristics of structural carbon steels, depending on the quantitative content of these elements, such alloys are divided into steels of ordinary quality, quality, high quality and high quality.
In structural carbon steels of these categories sulfur and phosphorus, contained in the following quantities:
- in alloys of ordinary quality (they can be distinguished by the marking "Century") - not more 0,05%;
- quality (referred to as "Steel") - no more than 0,035%;
- high quality (marked with the letter "A") - not more 0,025%;
- are of particularly high quality (marking - the letter "W") - not more 0,015%.
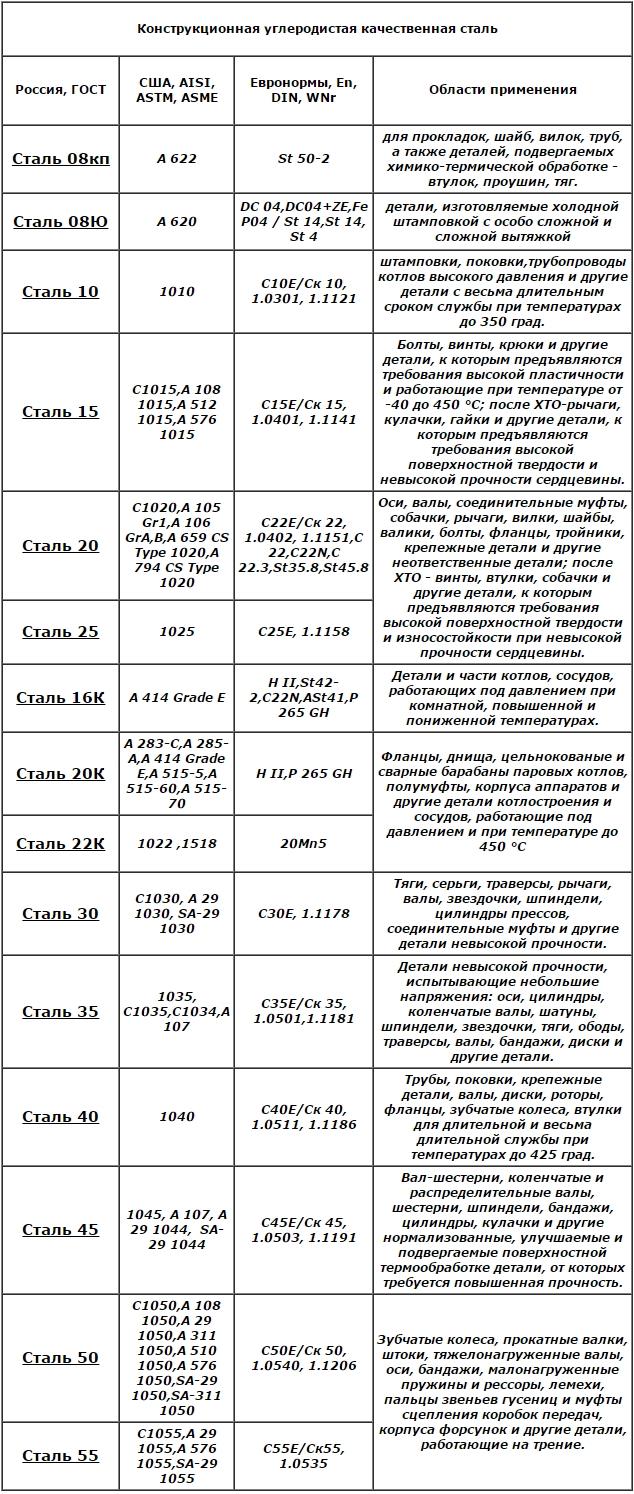
High-quality carbon structural steels and areas of their use
Carbon steels, relating to structural, are classified on other grounds, which will be discussed below.
Structural steels in the engineering industry
Features of chemical composition allow to allocate in structural steels, used for the manufacture of machine-building products, two large groups:
- low and medium carbon;
- low - and medium alloy.

Composition and properties of carbon engineering steels
Carbon steels, which are used for the production of various products in the engineering industry, must meet a number of qualitative and mechanical characteristics, to the most important of which are:
- impact strength;
- plasticity;
- strength.
The structure of most structural carbon steels, used for the manufacture of machine-building products, refers to the pre-eutectoid pearlitic type. The most popular brands of such steels are 30H2GSN2VM, 30HGSN2A, 40HN2SMA, 25H2GNTRA and others. To increase the viscosity of this type of carbon alloy, molybdenum and nickel are introduced into their composition.
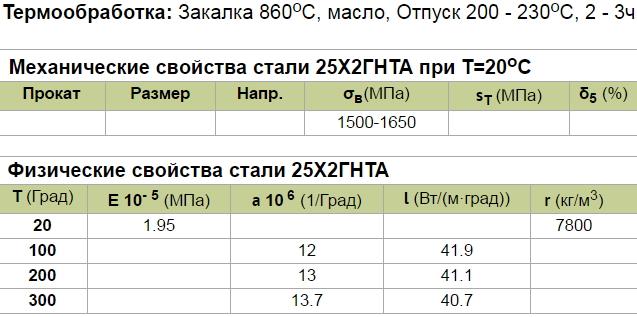
Steel of the 25X2GNTA brand is used for production of bolts, beams and vessels
Depending on the different types of machine-building structural steels are also subdivided, whether the products are reinforced, which of them are made. So, distinguish products:
- not amenable to strengthening;
- in which only the surface layer is subjected to hardening;
- in which the entire volume of metal is subjected to hardening.
Some brands of machine-building structural alloys (08kp, 15kp, St3 and others), of which mainly sheet metal is made, not subject to any heat treatment. Because this sheet metal is used for the production of various products by cold deformation, its plasticity is subject to increased requirements. This plasticity provides a minimum amount of silicon and carbon. In addition to the ability to deform well in the cold state, steels of these brands are characterized by excellent weldability.

Chemical composition of stamped steels
Structural steel alloys, belonging to the category of quality, must be heat treated:
- hardening of the surface layer, after which the metal can be released;
- hardening, performed by standard technology, after which the leave procedure is mandatory (the combination of these types of heat treatment of metal gives good weldability of products from it);
- metal normalization.
Brands and characteristics of machine-building structural alloys
Machine-building steels of special purpose can have a nickel or iron-nickel base. in addition, they are divided into the following categories:
- used for the production of products by casting;
- so-called automatic;
- differ in the increased wear resistance;
- with increased corrosion resistance;
- ball bearing;
- spring;
- differ in the increased heat resistance;
- cryogenic, do not lose the qualitative characteristics at influence of low temperatures;
- heat resistant.
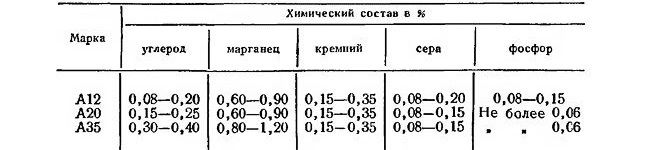
Brands of automatic steels
Heat-resistant steel alloys, in the chemical composition of which contains a small amount of silicon, can be successfully operated at temperatures, reaching 5500 Celsius. Such carbon steels, in addition to its heat resistance, differ in a number of significant characteristics: they are successfully operated in oxidizing and carburizing media, not subject to gas corrosion. They also have a serious drawback, which is manifested in that, that under the influence of considerable loadings they start to show creep.
The most popular brands of such steels are 12X17, 15X28, 15Х6СМ, 20X20H14C2 and others. They are used mainly for production:
- containers, in which cementation of steel details is carried out;
- parts of reciprocating engines;
- pipe products for various purposes.
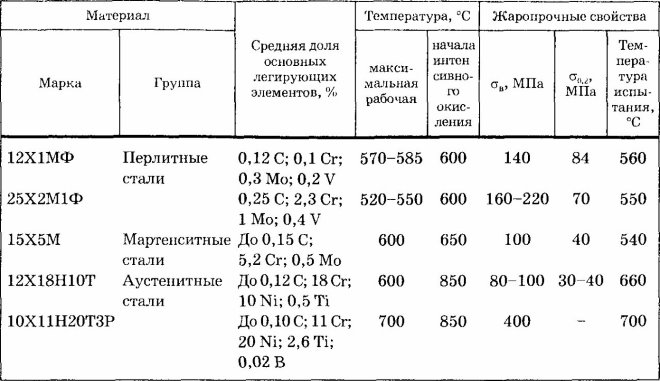
Properties of heat-resistant steels
To the group of cryogenic alloys, which are characterized by high viscosity and ductility, can be treated as low-carbon, and high-alloy steels. What is characteristic, creep of such steels increases not only at decrease in temperature of their operation, but also when performing heat treatment, which consists in the normalization and subsequent release. Marking of structural alloys of this type is regulated by the requirements of the relevant Guest (5632).
Structural carbon steels, belonging to the category of heat-resistant, have high creep. They are distinguished by this quality, as high resistance to chemical corrosion. These carbon steels are optimal for pipe production, parts of gas and steam turbines, operating at temperatures in the range 400-6500 Celsius. The most popular brands are 15XM, 15Х5М, 12Kh18N9T, HN70Yu and others.

Solid turbine rotor, made of 25H1M1FA steel
Structural carbon steels, belonging to the category of corrosion-resistant, differ in that, that they contain more 12,5% chromium. It is this element that makes it possible to successfully use them for the production of products, who are affected by aggressive environments (pipes for various purposes, carburetor shafts, steam turbine blades, etc.). Such steels can be of several types:
- with a martensitic structure (30Х13, 12Х13, 20Х17Н2, 95X18);
- from martensitic-aging (09Х15Н8Ю, 10Х17Н13М3Т);
- from austenitic and ferritic (12Х18Н10Т, 15X28 and others).
That products from structural carbon steels of all above-mentioned types are well welded, they must be on leave. Notable, what, despite significant differences in their qualitative characteristics, heat resistant, heat-resistant and cryogenic steels are corrosion-resistant alloys.
Features of other types of structural steels
Structural alloys, belonging to the category of wear-resistant, containing a significant amount of alloying additives, can be low - and high-carbon. From such steels, perfectly resist not only mechanical wear, but also cavitation corrosion, produce elements of crushing equipment, trucks, blades of pumping equipment, etc.. The most popular brands of these alloys are OX14AG12, ОХ14АГ12М, 12Kh18N9T, G13.
Carbon steels, which belong to the category of automatic (А40Г, AC40G2, AC45X and others), include various elements: 0,6-1.5% of manganese, 0,05-0.16% of phosphorus, 0,05-0.3% sulfur. Carbon in such alloys is contained in 0,45%. The addition of such elements allows to significantly improve their quality characteristics, as selenium, lead and calcium. From these structural carbon steels, which do not have high strength, produce parts for the automotive industry: bolts, hairpins, washers, etc.
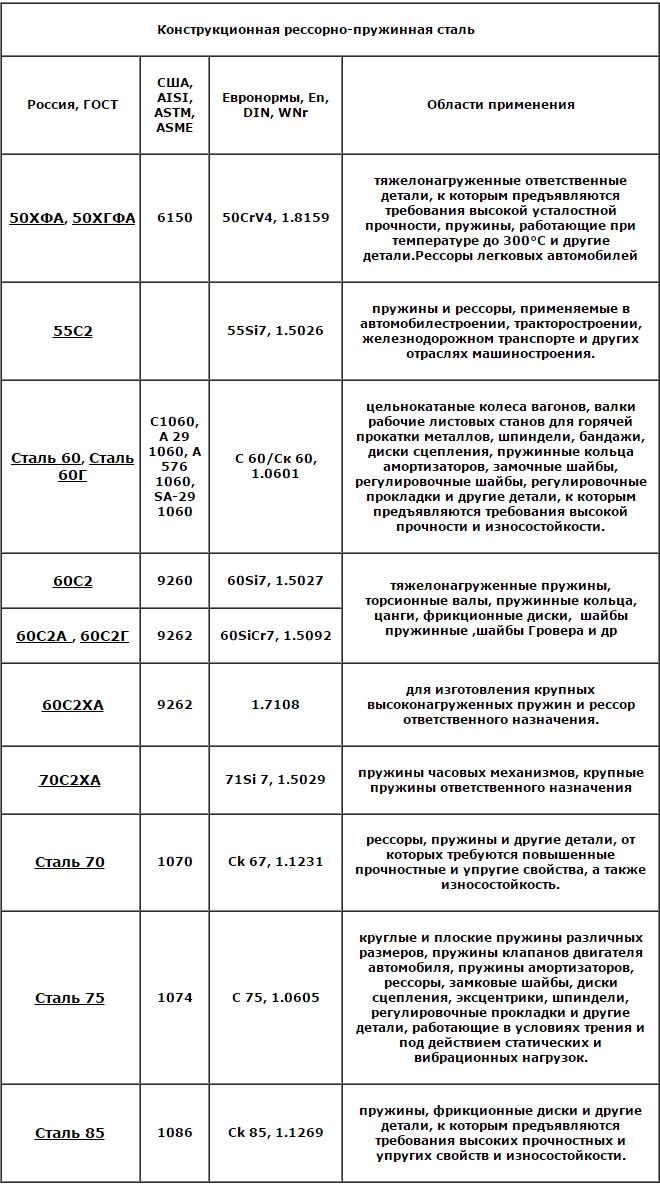
Areas of application of some spring steels
Elastic steel 50HFA, 55S2, 60S2HFA, 65GU, 70C2HA and others) in full accordance with their name are characterized by good viscosity and ductility, they are also characterized by high strength and elasticity. These include low-alloy, and medium carbon alloys, which contain 0.6-0.8% of carbon. When they are welded, cracks can form. Such steels are used for the production of springs and springs for various purposes.
Structural steels belong to the category of improved, the internal structure of which is martensite in the form of small needles. There are no non-metallic inclusions in the dense structure of such carbon alloys, as well as carbide insulation and mesh. The main advantages of these low-alloy and high-carbon steels (carbon content - up to 1,05%) there is increased hardness and wear resistance. A distinctive feature of the labeling of such alloys is that, that it always starts with the letter "W" (ШХ4, ШХ15Ш, SHH15SG and others).
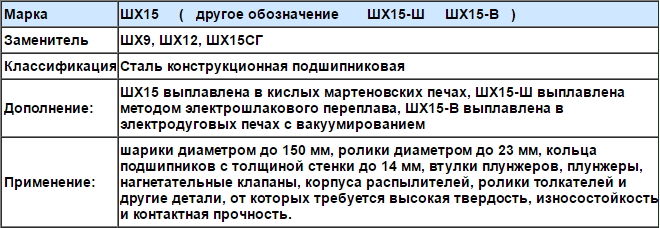
ShX15 steel is used for the production of products. which require wear resistance, high hardness and contact strength
Structural steels in construction
Structural carbon steels, used in construction, differ in a small amount of alloying elements (chromium, manganese and silicon), as well as carbon content in the range of 0.1-0.2%. Such steel, in addition to good weldability, endowed with the following characteristics, which are especially useful in the manufacture of building structures:
- good ductility and fluidity;
- high hardness and toughness;
- optimal parameters of relative elongation and strength.

In the construction of bridge crossings, overpasses use steel 10HSND, 15HSNDA, 16D GUEST 6713-91 and other
Production of products, used in the construction industry, not carbon, and from low-alloy steels allows to save considerably on the used raw materials (to 30%). Alloying such steels not only improves their hardening, but also increases the limit of their fluidity.
The most popular brands of these steels, delivered in the form of high-quality hire, letters, strips and rods, is:
- 14G2;
- 15ХСНД;
- 10G2C1;
- 18G2;
- 18G2C;
- 25G2C;
- 35GS.
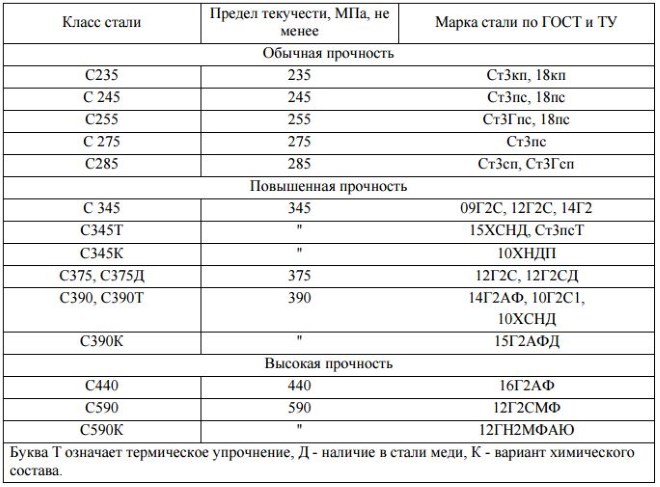
Steels for building constructions
As mentioned above, steels of this category are easily welded, as well as other processing methods, that allows to create from them building constructions of any size and a configuration without special labor costs.




