
Tighten the cylinder head bolts with a torque wrench

Tightening the cylinder head is an important and responsible procedure. This operation is performed during the reverse assembly of the engine, after removal of the cylinder head. Proper tightening of the cylinder head bolts affects the serviceability and efficiency of the power unit, since the head is part of the combustion chamber. In other words, after tightening the cylinder head is a single unit with the cylinder block. Between the block and the head of the block the sealing lining is in addition established. In that case, if the head is tightened incorrectly, high probability of damage to the cylinder head itself, gaskets, bolts of the head of the block and openings under bolts in BC.
We also recommend reading the article about it, what is engine overhaul. In this article you will learn about the features of engine overhaul, as well as its main differences from the search engine.
In some cases, leaks appear at the gasket installation site. Also in the case of a loose fit of the head of the unit during the operation of the internal combustion engine may be a breakthrough of exhaust gases into the channels of the lubrication and cooling system of the engine, and there is a hit of antifreeze in oil and vice versa. As a result, the properties of the lubricant and coolant change, which can quickly disable the engine. Next we'll talk about that, what is the procedure for tightening the cylinder head bolts to be followed, how to tighten the bolts of the cylinder head with a torque wrench, and what should be the tightening force of the head.
Tightening of a head of the block of cylinders on the diesel and the petrol engine

Regardless, what type of engine is installed on a particular car (diesel or gasoline), the cylinder head of modern cars has a similar device. This engine element consists of a housing, in which the timing mechanism is installed (camshafts, inlet and outlet valves). Another feature of the cylinder head is that, that part of the combustion chamber is made in the head. Special channels are also made in the head housing, on which motor oil and working liquid of cooling system circulates.
Proper fit of the head to the cylinder block ensures the tightness of the combustion chamber, channels of cooling and lubrication systems, as a result the power unit gives the maximum of power and a twisting moment, which provides better fuel economy and other critical performance characteristics. In that case, if the cylinder head is tightened incorrectly, cracks may appear in the head housing. The point is, that the cylinder head is made of aluminum alloys, while the head mounting bolts are steel.
With that in mind, that internal combustion engines are prone to significant heating during operation, internal combustion engine parts experience thermal expansion. As for the cylinder head, aluminum head and steel bolts expand in different ways. It turns out, if the head is tightened incorrectly, then in its case there is an uneven tension. For this reason, it is essential to observe the tightening torque of the cylinder head bolts, as well as the sequence of tightening the mounting bolts.
How to tighten the cylinder head correctly
Let's start with that, that to tighten the cylinder head you need to have a torque wrench. You should also prepare the appropriate wrench heads and have some clean engine oil. Before tightening the head mounting bolts, be sure to read the manual for repair and operation of a particular vehicle. This recommendation is especially important, since the tightening force of the bolts on different motors differs. Some engines have a cylinder block, which is made of cast iron, while other internal combustion engines receive lightweight blocks of aluminum alloys.
Moreover, even on different motors from the same manufacturer with aluminum head and cast iron block, the degree of tightening of the head will still be different. Also in the manual the order of tightening of fastening bolts will be specified also. Turning to the process of tightening the cylinder head, should be remembered, that each action occurs sequentially. The main goal is, that tightening was carried out evenly. The main recommendations are discussed below.
- It does not matter when installing the head and then tightening, whether you put the assembled part or mount one case.
- At the initial stage, you need to lubricate the mounting bolts with engine oil. To do this, apply a small amount of oil to the bolt thread.
- Then the bolts are inserted into the holes, made in the body of the head and cylinder block, then tightened by hand.
- Next, the torque wrench should stretch the bolts in a certain sequence and with the specified in the manual tightening torque. Usually the delay is carried out in several approaches. Initially, the bolts are tightened with little effort, then additionally stretch one or two more times.
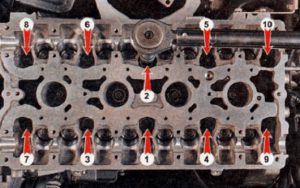
- Also remember, which is especially important to follow not only the effort, but also the order of tightening the bolts. Example, during installation of the cylinder head on in-line internal combustion engine tightening of fastening bolts is made from the center to edges of a head. This approach reduces the risk of damage to the head of the unit, and gaskets between BC and cylinder head.
- It is worth adding, that after the run is close 1000 km on some cars the bolts need to be tightened. It depends on certain design features of a particular engine. If the so-called spring mounting bolts were used during tightening, then tightening after the installation of the cylinder head is not required.
Common mistakes when tightening the head
Note, that errors during the installation of the cylinder head can lead to damage to the head and the cylinder block. Also, after the start of operation of the internal combustion engine, serious malfunctions may occur, which are able to quickly disable the engine. In some cases, the power unit can be damaged so much, requiring major repairs or replacement of such a motor with a contract engine. In the list of various errors, which lead to undesirable consequences, should be singled out: tightening bolts, ingress of engine oil into the holes for mounting mounting bolts, work with inappropriate or worn nozzles on the torque wrench, violation of the order of tightening the bolts, use of bolts, which do not fit in size.
Quite often the hole under the mounting bolt in the cylinder block is clogged with dirt, rust, etc.. P. Attempts to clean the hole do not always give a positive result. As a result, it can be very difficult to tighten the bolts with proper effort. For this reason, the thread of the bolts is lubricated with oil. It is forbidden to pour oil into the hole to improve lubrication. Such actions can lead to that, that the threaded well will simply collapse after tightening the bolt. In this situation, the cylinder block will need to be repaired or even replaced.
An attempt to tighten the cylinder head without the use of a torque wrench can also cause problems. In this case, the tightening torque is often exceeded. The consequences can be very different, but most often the head mounting bolts break, then there is a need to re-disassemble the engine to remove debris and repair the cylinder block.
We also recommend reading the article about it, how to repair a crack in the cylinder block and cylinder head. In this article you will learn about different ways to repair cracks BC and cylinder head.
Bolts for tightening the cylinder head usually have a nozzle under the hexagonal head, less often performed in the form of a square. If the nozzle is worn, then there is a risk of turning it over during tightening. As a result, the faces of the bolt head "lick". In this situation, the damaged fastener is difficult to tighten or unscrew to replace. As for the selection of bolts, it is necessary to take into account some features. You can find information on this in many repair manuals, that the bolts may be reused. As practice shows, it is optimal to change the fasteners for new ones after each removal of the cylinder head.
The point is, that after tightening the bolt becomes a little longer, that is, extracted. For this reason, pay attention to the maximum allowable bolt length, which must be specified in the operation manual. If there are no new bolts, then the existing fasteners must be measured before installation. In that case, when the bolt is slightly longer than the maximum allowable value, then it stops at the bottom of the hole in the cylinder block. The result is either a bolt breakage, or splitting of the cylinder block.
Violation of the order of tightening of fastening bolts recommended in the repair manual of the concrete engine causes excessive overvoltage in the case of a head of the block of cylinders. Aluminum alloys, which are the material of the cylinder head, not adapted to such loads. The result is the appearance of cracks in the body of the head. Gases leak through small cracks, that is, the tightness of the combustion chamber is violated. The engine in this case loses power, there is increased fuel consumption. If cracks affect the channels of the lubrication or cooling system, then oil or antifreeze may enter the combustion chamber, as well as possible external leaks.
Finally, let's add, that it is possible that the working fluids from one system to another (example, the antifreeze enters the oil channels). Faults of this kind are quite serious, as disturbances in the normal operation of the lubrication or cooling system lead to overheating of the internal combustion engine, accelerated wear of friction parts, jamming of the engine, etc.. d.




