
Heat resistant steel: grade and composition of heat-resistant steels and alloys
Heat resistant steel, represented in the modern market by a wide variety of brands, as well as heat-resistant alloys, is recognized by most experts as the best material for the manufacture of structural elements and equipment, which are operated in constant contact with aggressive environments and in other difficult conditions.

Typical heat-resistant steel products are furnaces, fireplaces, boilers and metal chimneys
Heat resistance and heat resistance of metal
Heat resistance, which is possessed by steels and other metal alloys of a separate category, has another name - "scale resistance". This is a property, which individual metals are given in the production process, is their ability for a long time in high temperatures to actively resist such a negative phenomenon, as gas corrosion. Unlike heat-resistant, heat-resistant steels and metals of other types have the ability not to collapse and deform under prolonged exposure to high temperatures.
A brief digression in video format about the features of heat-resistant steels and their differences from other alloys.
Metals, which are heat resistant, used mainly for the manufacture of unloaded structures, operated under conditions of constant exposure to gaseous oxides and temperatures, not exceeding 550 °. To such constructions, in particular, include elements of heating furnaces.
Alloys, made on the basis of iron, even if they are heat resistant, under such operating conditions and under the influence of temperature, exceeding 550 °, begin to actively oxidize, which leads to the appearance of a film on their surface, consisting of iron oxide. The chemical compound of iron and oxygen formed on the surface of such metal is, essentially, brittle scale. It is characterized by an elementary crystal lattice, containing an insufficient number of atoms of the second substance.
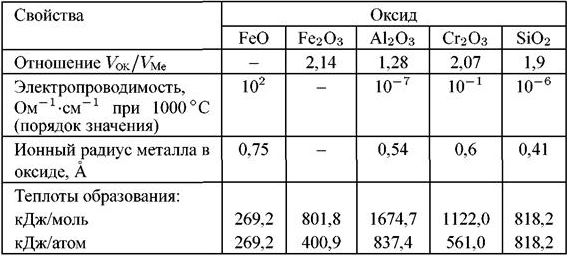
Properties of oxides of elements, increasing the heat resistance of iron
To improve this property of steel, as heat resistance, its chemical composition is chromium, aluminum and silicon. Combining with oxygen, these elements contribute to the formation of dense and reliable crystalline structures in the metal structure, which improves its ability to painlessly tolerate the effects of elevated temperatures.
The number and type of alloying additives, introduced into the chemical composition of the alloy, made on the basis of iron, depends on the temperature conditions of operation of the products, which will be made of it.
Steels show better heat resistance, alloying which is made on the basis of such metal, like chrome. To the most famous brands of such steels, which are called sylchromes, include:
- 08Х17Т;
- 15Х25Т;
- 15Х6СЮ;
- 36Х18Н25С2.
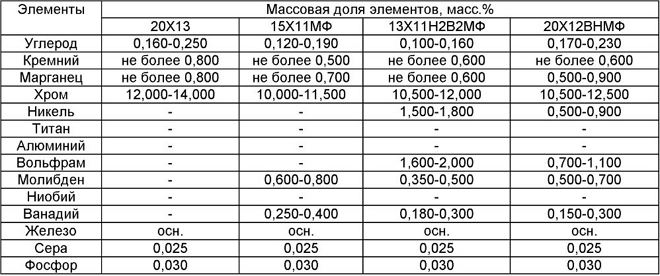
Chemical composition of heat-resistant steels of grades 13Х11Н2В2МФ, 15Х11МФ, 20Х13, 20Х12ВНМФ
What is characteristic, heat resistance of steel increases with increasing chemical content of chromium. Using this metal as an alloying element, you can create steel grades, products from which will not lose their original characteristics even with prolonged exposure to temperature, exceeding 1000 degrees.
Features of materials with heat-resistant properties
Heat-resistant steels and alloys, as mentioned above, are able to operate successfully in conditions of constant exposure to high temperatures, while not showing a tendency to creep. The essence of this negative process, to which subjects of usual marks and other metals became, is, that material, which is affected by constant temperature and constant load, begins to deform slowly, or crawl.
Creep, which are trying to avoid them, creating heat-resistant steels and metals of another type, there are two types:
- lasted;
- short-lived.
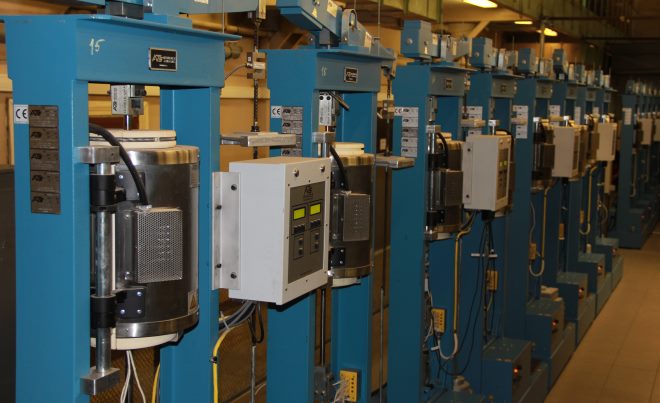

A set of test machines is used to determine the creep of alloys in research centers
To determine the parameters of short-term creep, materials are subjected to special tests, for which they are placed in the oven, heated to a certain temperature, and apply to them a tensile load. This test is performed for a limited period of time.
Check the material for its tendency to long-term creep and determine such an important parameter, as the limit of creep, in a short period of time will not work. To do this, the test product, placed in the oven, it is necessary to subject to long loading. The importance of such an indicator, as the creep limit of the material, is, that it characterizes the greatest stress, which leads to the destruction of the heated product after exposure for a certain period of time.
Marks of heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels
Steel, heat resistance and heat resistance differ, the state of the internal structure are divided into several categories:
- austenitic;
- martensitic;
- pearlitic;
- martensitic-ferritic.
At the same time steel, belonging to the category of heat-resistant, can be represented by two types:
- ferrite;
- austenitic-ferritic or martensitic.
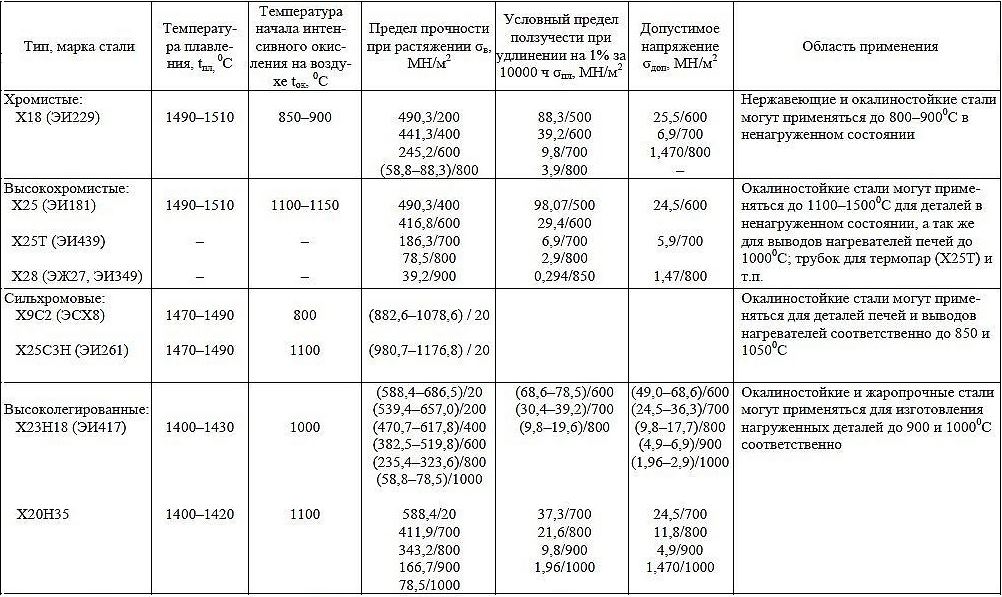
The main properties of some heat-resistant steels (click to enlarge)
If we consider steels with a martensitic internal structure, then their most famous brands are:
- X5 (pipes are made of such heat-resistant steel, which are expected to operate at temperatures, not exceeding 650 °);
- Х5М, Х5ВФ, Х6СМ, 1Х8ВФ, 1Х12Н2ВМФ (used for the manufacture of products, operated at 500-600 ° for a certain period of time (1000-10000 hours));
- 3X13H7C2 and 4X9C2 (products of these brands can be successfully operated at 850-950 °, therefore from such steels make valves of engines of vehicles);
- 1Х8ВФ (heat-resistant steel products of this brand can be successfully operated at temperatures, not exceeding 500 °, for 10000 hours and even longer; from this material, in particular, produce structural elements of steam turbines).
Heat-resistant steel sheet is used there, where good resistance to high temperatures and aggressive environments is required

The basis of the martensitic structure of steel is perlite, which changes its state in that case, if the composition of the material to increase the quantitative content of chromium. Pearlitic are the following brands of heat-resistant and heat-resistant steels, belonging to chromium-molybdenum and chromium-silicon: X6C, Х6СМ, Х7СМ, H9S2, Х10С2М and Х13Н7С2. To obtain from these steels a material with the internal structure of sorbitol, which has a high hardness (no less 25 units on the HRC scale), they are first hardened at 950-1100 °, and then subject to leave.
Steel alloys with ferritic internal structure, belonging to the category of heat-resistant materials, containing in its chemical composition from 25 to 33% chromium, which determines their characteristics. To give such steel a fine-grained structure, products from them are subjected to annealing. Steels of this category include grades 1Х12СЮ, H17, 0Х17Т, Х18СЮ, X25T and X28. It should be borne in mind, that when heating these steels to 850 ° and above, the grain in their internal structure begins to increase, which leads to an increase in their fragility.

Heat-resistant stainless steel is used in the production of sheet metal, seamless pipes and various units of the food and chemical industries
Become, the basis of the structure of which are martensite and ferrite, are actively used for the production of products for various purposes, used in the engineering industry. Ware, for the manufacture of which such heat-resistant alloys are used, even for a long time can be successfully operated at temperature, which is within 600 °. The most common brands of these heat-resistant steels are X6SYU, 1Х13, 1Х11МФ, 1Х12В2МФ, 1Х12ВНМФ, 2Х12ВМБФР. Such heat-resistant alloys differ in that, that chromium in their chemical composition is contained within 10-14%, but light additives, by means of which improve their chemical composition, is tungsten, molybdenum and vanadium.
Austenitic and austenitic-ferritic steel alloys
The most significant features of austenitic steels are, that their internal structure is formed due to the presence of nickel in their composition, and such a property, as heat resistance, due to the presence of chromium. In alloys of this category, characterized by low carbon content in its chemical composition, in some cases there may be such alloying elements, both niobium and titanium. Become, the basis of the internal structure of which is austenite, belong to the category of stainless steel, and with prolonged exposure to high temperatures (to 1000 degrees) successfully resist the formation of a scale layer.

Austenitic alloys of the H17H13M2 and H17H13M3 brands are optimally suitable for designs, working under the influence of acids
The most common to date, steels with austenitic internal structure are alloys of dispersion-hardening category. To improve the quality characteristics of their composition add intermetallic or carbide seals, depending on what such materials and belong to a certain category.
The most popular brands of heat-resistant steels, the basis of the internal structure of which is austenite, is:
- dispersion-hardening Х12Н20Т3Р, 4Х12Н8Г8МФБ, 0Х14Н28В3Т3ЮР, 4Х14Н14В2М (of these heat-resistant steels, belonging to the category of stainless steel, make constructive elements of turbines and valves of engines of vehicles);
- homogeneous 1X14H16B, 1Х14Н18В2Б, Kh18N12T, Х18Н10Т, Х23Н18, Х25Н20С2, Х25Н16Г7АР (from materials of these brands mainly make fittings and pipes, operated under the influence of significant loads, ultra-high pressure units, elements of exhaust systems).
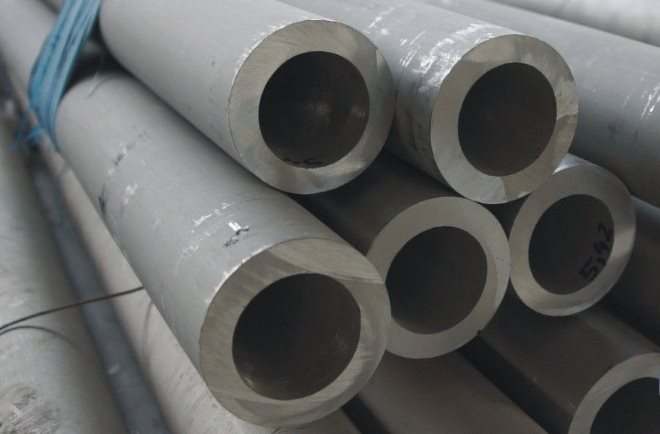

Heat-resistant pipe from steel of the 20X23H18 brand (it is H23H18 or EI417) used for the manufacture of furnace equipment, forgings and bandages
Steel alloys, the basis of the internal structure of which is a mixture of austenite and ferrite, differs in exceptional heat resistance, which exceeds in its performance a similar parameter, even high-chromium materials. Such heat resistance characteristics are achieved due to the highest stability of the internal structure of steels of this category. Products from them can be successfully operated even at temperatures, reaching 1150 °.
Meanwhile, for heat-resistant steels with austenitic-martensitic internal structure is characterized by increased brittleness, therefore, they cannot be used for the production of products, operated under high load.
Products of the following purpose are made of heat-resistant steels of this category:
- pyrometric tube (Х23Н13);
- conveyors for furnaces, heat-resistant pipes, tanks for the cementation procedure (Х20Н14С2 and 0Х20Н14С2).
Steels and metals, characterized by refractoriness
Steel alloys, which are based on refractory metals, used for the manufacture of products, operated at 1000-2000 °.
Refractory metals, included in the chemical composition of such steels, characterized by such melting temperatures (div. table).
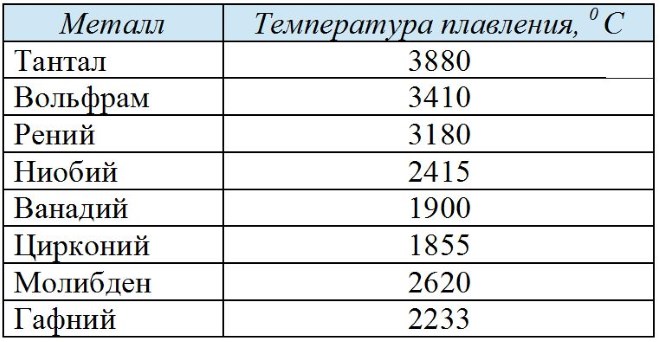
Melting point of refractory metals
Due to that, that refractory steels of this category are characterized by a high temperature of transition to a brittle state, at considerable heating they are deformed. To increase the heat resistance of such steels, their chemical composition is found in special additives, and to increase heat resistance they are alloyed with such elements, like titanium, molybdenum, tantalum, etc..
The most common ratios of chemical elements in refractory alloys are:
- base - tungsten and 30% rhenium;
- 60% vanadium and 40% niobium;
- basis - 48% iron, 15% niobium, 5% molybdenum and 1% zirconium;
- 10% tungsten and tantalum.
Alloys based on nickel and a mixture of nickel and iron
Nickel-based alloys (55% nickel) or made on the basis of a mixture of Nickel and iron (65%) are heat-resistant and have decent heat-resistant qualities. The basic alloying element for any steel of this category is chrome, which they may contain from 14 to 23%.
If we talk about stability and strength, high rates of which persist at elevated temperatures, then steel alloys have such qualities, made on the basis of nickel. The most popular of these are HN60V, ХН67ВМТЮ, ХН70, ХН70МВТЮБ, KhN77TYu, ХН78Т, ХН78Т, ХН78МТЮ. Some of these steel grades are heat resistant, and the rest - heat-resistant. When heated on the surface of products from alloys of these brands appears oxide film based on chromium and aluminum, and in solid solutions of the structure of such metals are formed compounds of aluminum with nickel or titanium with nickel, which ensures the resistance of such materials to high temperatures. You can get acquainted in more detail with the characteristics of heat-resistant alloys on the nickel group, having studied special reference books.

Rotary shafts made of heat-resistant nickel alloy
Nickel steel groups are used for manufacturing:
- elements of gas structures and communications (ХН35ВМТЮ; an example of products for this purpose is a heat-resistant pipe);
- structural elements of turbine devices (ХН35ВТР);
- structural elements of compressors - blades and disks (KhN35VTYu);
- rotors, which equip turbines (HN35VT and HN35VMT).
In conclusion, an informative video about the intricacies of production and processing of steel at home.




