
Argon welding - technology and equipment for argon welding
When it is necessary to form a permanent connection of stainless steel parts, copper, titanium, aluminum, as well as a number of other non-ferrous metals and alloys based on them, argon welding is most often used. The process of its implementation is quite time consuming and specific.

The process of welding in argon
Principles of welding, performed in argon
Argon welding combines the features of electric arc and gas welding. With electric arc welding, this technological process combines the mandatory use of an electric arc, and with gas - the use of gas, as well as some technological methods of forming an integral connection.
Melting of edges of connecting parts and filler material, by means of which the weld is formed, provided by high temperature, created by the combustion of an electric arc. Gas (in this case argon) performs protective functions, what to talk about in more detail.
Welding of alloy steels, most non-ferrous metals and alloys based on them have some features, which are, what, being in the molten state, interacting with oxygen and other impurities in the air, such metals are actively oxidized.
This negatively affects the quality of the molded weld: it turns out to be fragile, in its structure pores are formed - air bubbles, which significantly weaken the connection. Even more negative impact of the surrounding air on aluminum, molten in the process of welding. Under the influence of oxygen, located in the surrounding air, this metal begins to burn.
The best solution, that allows to protect effectively a zone of the formed connection at welding of metals of color group and alloy steels, there is a use of shielding gas - they are argon. The high efficiency of this gas is due to its characteristics.
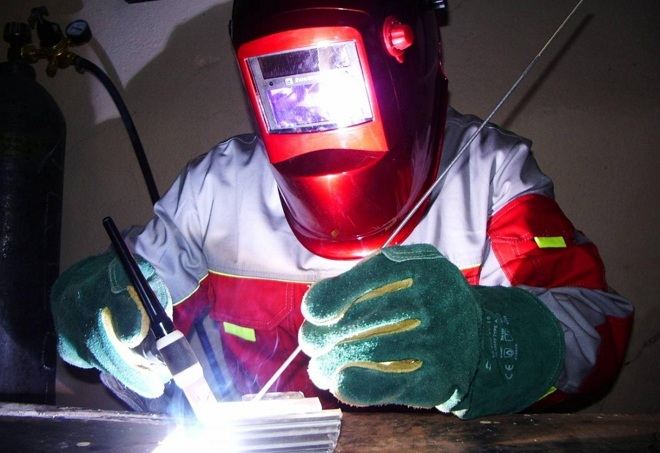
Argon arc welding scheme
Argon is much heavier than air (on 38%), therefore, it easily expels air from the welding area and creates reliable protection. Being inert by nature, argon practically does not react with molten metal, as well as other gases, present in the area, where the welding arc burns. One important point should be considered when reverse polarity argon welding: electrons are easily separated from gas atoms in this case, the flow of which converts the gaseous medium into a conductive plasma.
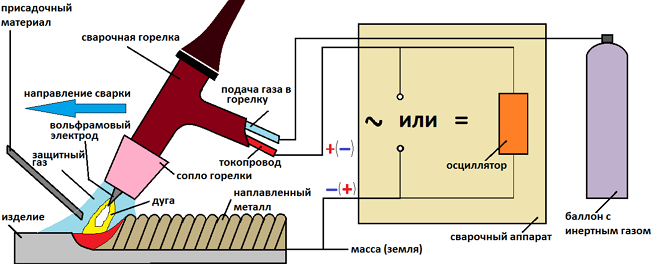
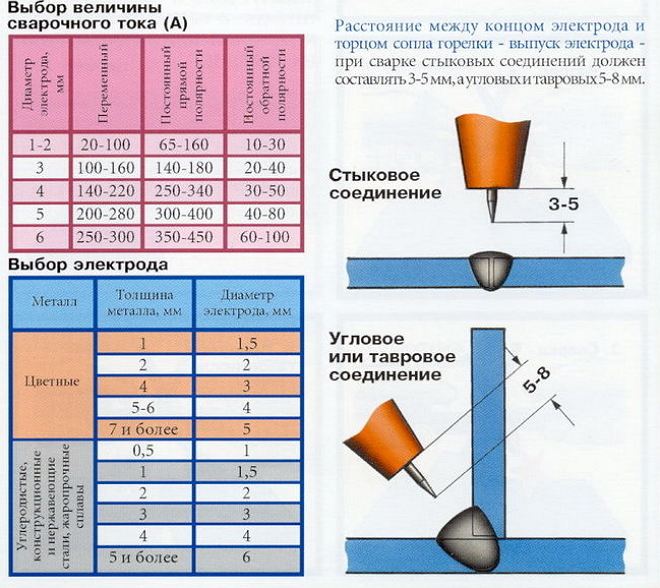
Technology of welding in the environment of such gas, as argon, may involve the use of melting, as well as non-melting electrodes (such are tungsten rods). Diameter of tungsten electrodes, which, as you know, differs in exceptional refractoriness, selected according to special directories. The choice of this parameter is influenced by the characteristics of the connecting parts.
Argon arc welding methods
Argon welding is divided into three types depending on the technology used:
- manually, performed by a non-fusible tungsten electrode (this technology is abbreviated RADIUM);
- automatic, passing in an argon environment using non-melting electrodes (designation of welding of this type - HELL);
- automatic, performed in an argon environment using fusible electrodes (the name of this technology is ADP).
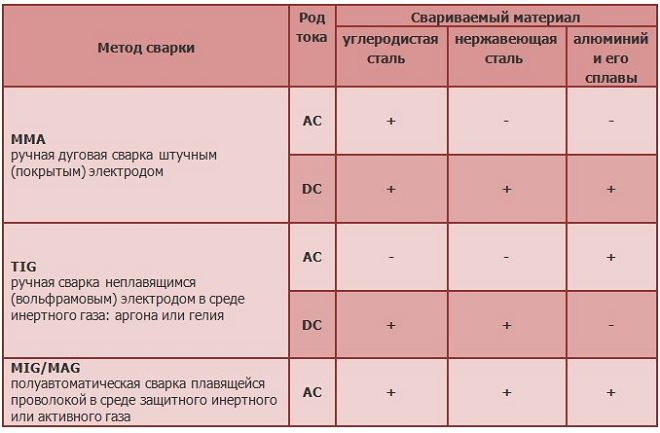
According to the international classification, argon arc welding or welding machine, performed using a tungsten electrode in a protective medium of any inert gas, is denoted by the abbreviation TIG (Tungsten inert gas).
Features of welding in argon
Working body of welding equipment, which is used to connect metal parts in a protective gas environment (including argon), there is a burner. It is in the burner (in its central part) a tungsten electrode is inserted, departure of which must be within 2-5 mm Fixation of the electrode inside such a burner is provided by a special holder: you can insert a tungsten rod of any desired diameter. To supply shielding gas, the welding torch is equipped with a ceramic nozzle.
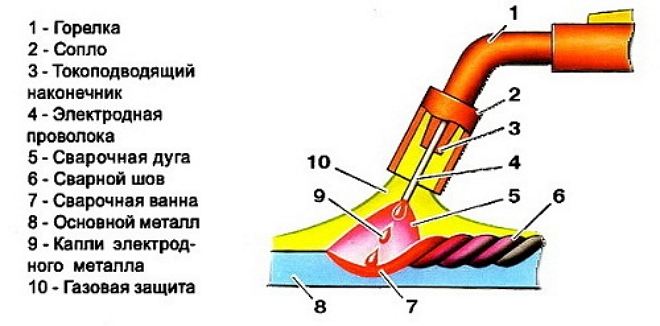
The principle of argon welding
The required temperature during argon welding, as mentioned above, creates an electric arc. The weld is formed with the help of filler wire, the composition of which should correspond as much as possible to the composition of the processed metal.
We list the main stages of welding of this type, which uses a tungsten electrode.
- The surfaces of the joined parts are thoroughly cleaned of dirt, traces of grease and grease, as well as from the oxide film. Such cleaning is mandatory and can be performed mechanically or by chemical means.
- The "ground" must be connected to the connecting parts. You can do this directly (if the parts are large), and with the help of a metal desktop surface (if the parts are not large). Filler wire, which is important, not included in the electric welding circuit, and served separately.
- The welding current is set on the welding equipment. This parameter is selected depending on the characteristics of the workpieces to be joined.
- After switching on the current, the burner with the electrode is brought to the welded parts as close as possible, without touching their surface. Optimal distance, on which the burner is placed from the surface of the connected workpieces (it must be maintained during welding), – 2 mm. Keeping the electrode at such a short distance allows you to melt well the mating metal, get a beautiful and neat weld.
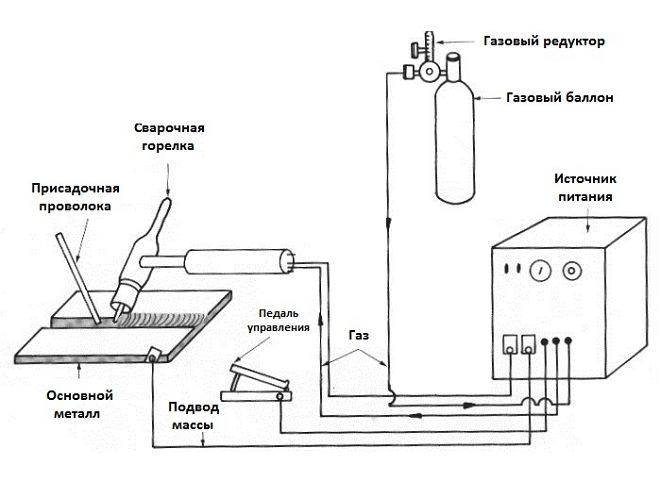
Scheme of welding equipment for welding in argon
- Supply of shielding gas include advance - for 15-20 seconds before welding. Turn off the argon supply not immediately after welding, and a little later - through 5-10 seconds.
- The burner and filler wire slowly lead only along the seam formed, without making them transverse oscillations. Additive wire, which is located in front of the burner, injected into the area of electric arc very smoothly, without making sudden movements. Otherwise, the molten metal will be highly sprayed.
- When performing welding, the electric arc is ignited, without touching the electrode to the connecting surfaces. This rule must be followed for several reasons. Firstly, the ionization potential of argon is very high, which prevents it from effectively using the spark from the touch of the electrode. When a melting electrode is used for welding, metal vapors are formed when it touches the connecting parts. Their ionization potential is much lower, compared with argon, which facilitates the ignition process of the electric arc. Secondly, if the tungsten electrode touches the surface of the parts to be joined, it is polluted, which interferes with the quality of welding.

The process of argon arc welding nearby
Many have a natural question about that, how an electric arc can be ignited in the environment of such a gas, as argon, if its ionization potential is too high, and the electrode itself does not touch the surface of the connected parts. An oscillator is used for this purpose, which converts current from the mains current with typical parameters into high-frequency pulses with a voltage value 2000-6000 In and current frequency 150-500 Hz. Such impulses also give the chance to ignite an electric arc without contact of an electrode with connecting details.
Argon welding equipment and supplies
The presence of a standard welding machine is not enough to perform argon welding, which can be an inverter or transformer. This technology requires the use of such equipment and special equipment, as:

Inverter welder st and gas cylinder for argon welding
- inverter or conventional welding transformer, the capacity of which should be sufficient to perform such a technological process (in particular, a transformer can be used for this purpose, idle power which is in the range 60-70);
- power contactor, through which the required welding voltage will be applied to the welding torch;
- oscillators, the purpose of which was mentioned above;
- special regulator, which will be responsible for the cooling time of the welding zone with argon (as the shielding gas must be supplied a few seconds before the start of welding, and its supply must be closed a few seconds after its completion);
- special burner with ceramic nozzle and clamp for fixing the tungsten electrode;
- gas cylinder and reducer, which regulates the level of argon pressure, supplied to the welding zone;
- tungsten electrodes and filler rods of the required diameter;

Repair of alloy wheel - a variant of typical use of argon welding
- additional transformer, which is responsible for supplying voltage to switching devices;
- rectifier, producing direct electric voltage with voltage 24 V, which is fed to switching devices;
- relay, which is responsible for turning on and off such devices, both oscillators and contactor;
- electric gas valve, working from voltage 24 in or 220 V;
- inductive-capacitive type filter, which protects the welding machine from the negative effects of high-voltage pulses;
- ammeter, used to measure the amount of welding current;
- working or faulty car battery capacity 55-75 Ah, which is necessary for that, to reduce the DC component of the welding current, necessarily occurs when performing the process on alternating current (such a battery is connected to the electric welding circuit in series);
- welding goggles, which must be used as the main element of protection of the welder.
If desired, equipment for argon welding can be completed with your own hands, buying all the necessary components in a hardware store or market. If you do not want to do design, then you can immediately buy a welding machine, whose brand has the abbreviation TIG. To start using such a device, it must be additionally equipped with a gas cylinder, burner, elements, which control the burner and the supply of shielding gas.
Recommendations for choosing modes
That welding with use of argon was executed qualitatively, you need to choose the right modes.
Important parameters when performing welding with this technology are the polarity and direction of electric current. Their choice is influenced by the properties of materials, to be welded. Alternating current or reverse polarity is chosen, when it is necessary to perform welding of details, made of aluminum, beryllium, magnesium and other non-ferrous metals. This choice is explained by the topic, that when using such parameters of electric current there is an effective destruction of an oxide film, which is always present on the surface of these materials.
Nuances of working with argon welding
A typical example is the welding of aluminum oxide film on the surface of which has a very high melting point. When welding parts of this metal on the reverse polarity current, the effective destruction of the oxide film is due to the fact, that argon ions actively bombard the surface of parts, connecting. Argon is converted into conductive plasma, which not only simplifies welding, but also significantly improves their quality. If welding of details from the given metal is carried out on alternating current, then to achieve this effect, the connecting parts must act as a cathode.
Such additional equipment is often used for welding in shielding gases, as oscillators. When performing welding using alternating current, it facilitates the ignition process of the welding arc, and when it lights up, acts as a stabilizer.
At that moment, when there is a change in the polarity of alternating current, deionization may occur (so, and attenuation) welding arc. That this did not happen, oscillators in moments of change of polarity of an electric current generates electric impulses and gives them to a welding arc.
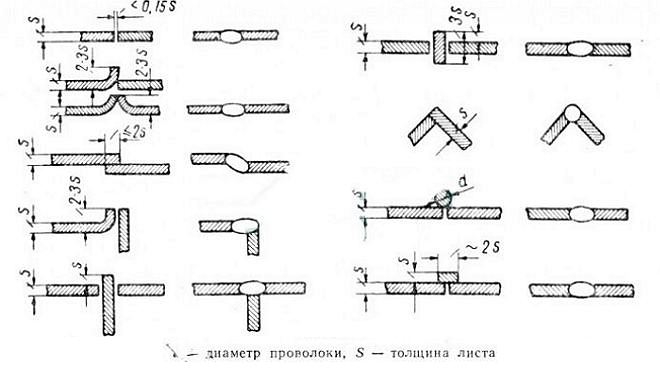
Types of sheet metal joints in argon arc welding
The value of welding current is chosen depending on a number of parameters: properties of the processed material, geometric dimensions of the workpieces, as well as the size of the electrodes used. It is best to use data to select this option, contained in special literature.
An important parameter is the consumption of shielding argon gas, which is selected depending on, at what speed is the supply of filler material and how fast are the demolition air streams. The minimum value of this parameter will be in that case, if welding is performed indoors, in which there are no drafts. If the process takes place outdoors, where strong gusts of crosswind are frequent, it is necessary not only to increase the consumption of argon, but also to use for its giving in a welding zone special confusing nozzles, gas from which is fed through fine pores.
In a protective gas mixture, except argon, often add oxygen in small quantities (3-5%). Oxygen in this case reacts with various harmful impurities, which may be present on the surface of the parts to be joined (moisture, dirt, etc.). As a result of this interaction, harmful impurities burn or turn into slag, popping up on the surface of the weld.
It should be borne in mind, that you can not use oxygen when performing copper welding, because the result is copper oxide. This connection, reacting with hydrogen, contained in the surrounding air, to form water vapor, which seeks to get out of the weld metal. All this leads to the appearance of many pores in the molded weld, which in the most negative way affects its qualitative characteristics.
Advantages and disadvantages of welding in a protective environment of argon
Welding is performed in a protective argon gas environment, has both advantages, and shortcomings, which must be taken into account. The advantages of this technology include:

Example of a seam, performed by welding in argon
- the possibility of obtaining a quality and reliable welded joint, which is provided by effective protection of the area of welding;
- slight heating of parts, connecting, which makes it possible to use this technology for welding parts of complex configuration (while they are not deformed);
- possibility to use for connection of details from materials, which cannot be cooked in other ways;
- significant increase in the speed of welding due to the use of high-temperature electric arc.
The disadvantages of this technology are:
- use of complex welding equipment;
- the need for special knowledge and sufficient experience in performing such work.
The use of argon welding allows to obtain high-quality and reliable welded joints, characterized by uniform melting of the connected parts. Using this technology, it is possible to weld details from non-ferrous metals of small thickness even without application of a filler wire.




