Reverse and direct polarity when inverter welding, the difference in polarity during welding
Electric arc welding method, unlike traditional gas, differs in some features. One of the most important is the heating temperature of the arc, which can reach 5000C, which significantly exceeds the melting point of any of the existing metals. This partly explains the great variety of technologies and methods of this type of welding, which allow you to solve various problems with its help.

Types of welding
Welding machines have a block of rectifying diodes. That creates a direct current, this is a must for semi-automatic welding machines, the material for which is wire. If the device requires electrodes, this means that all their models can be used during operation. And polarity during welding is a guarantee of its quality.
Using a semiautomatic device, the polarity of the connection must be observed. Welding under gas protection of the copper-plated wire occurs by means of direct polarity of current. In fact, it means:
- on a detail there is a plus;
- on the handle is a minus.
The current is applied to the part from the wire, and it heats up, unlike welding wire, stronger. As a result, the area of the welded area increases. It needs significant heating to form a cooking bath. Wire, having a smaller dissection, melts faster and gets to the desired area already liquid drop. Current, which passes from different polarities, captured molten material, the corresponding bath for welding turns out.
Using a semiautomatic device without a protective gas environment, you need to use a special flux-cored or flux-cored wire. In this case, the polarity of the connection between the handle and the "mass" changes. On the "mass" is a minus, and on the handle is a plus. The melting point of the flux wire is about the same, as well as the melting point of the metal. To achieve a quality seam, necessary, to burn the flux. Then there are two such processes:
- The appearance of a gaseous cloud;
- Welding takes place in the environment of this cloud.
The current changes from minus to plus, and the drop of the liquid drop of metal becomes lower. This causes less heating of the metal for welding. Since its cooling does not occur under the protective gas. Therefore, the formation of the bath for welding is almost no different from welding in a gaseous medium. AC operation has certain advantages. It does not diverge from the arc relative to the initial axis. And the quality of the connection is affected by the deviation of the arc.
Doing welding with an alternator, easy to notice: its polarity changes cyclically. Cycles have a frequency 50 Hertz. She, rising to positive voltage, may drop to zero or fall to a negative level. The voltage changes from plus to minus and vice versa.
Welding of stainless steel and non-ferrous metals
When welding non-ferrous metals, including aluminum, use a special tungsten electrode. And used during inverter welding of direct polarity at the electrode is a minus. This type of connection allows you to have the required temperature in the heating area. This is important for aluminum, because the oxide film must be overcome first, in which the melting point is much higher, unlike the metal itself.
Polarity during welding directly contributes to the formation:
- better seam;
- better metal melting, including stainless steel;
- more concentrated narrow electric arc.
There is also an important economic part to the process. Using an expensive tungsten electrode of smaller diameter, along the way seek to reduce gas costs. If you connect a tungsten electrode when welding in a different polarity, namely, on the holder - with a plus, then the seam will not be so deep. This method has its advantages. Working with thin plates, you can not worry, that you will burn through a product from stainless steel and non-ferrous metal.
A significant disadvantage is the effect of electromagnetic blowing. The resulting arc is wandering, and the seam is not very attractive and airtight. Using alternating current, it is necessary to use electrodes for a break. Experienced welders usually choose DC. Thanks to him, welding creates a unidirectional passage of electrons. Polarity affects the quality of welding, including stainless steel material.
Direct polarity welding
Welding of direct polarity by the inverter turns out, if the "plus" current source is connected to the part. When the electrode is connected, then in this case the opposite polarity is obtained. Using a welding inverter, you can set the polarity on it yourself. Polarity determines the direction of movement of the electron flow. That is, determined by connecting the wires to the positive and negative terminals. When working with welding, the opposite polarity indicates:
- on the electrode - plus;
- on the "ground" - minus.
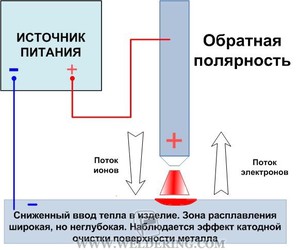
The current changes from negative to positive contact. That is why electrons pass to the electrode from the metal. As a result, the end of the electrode is heated. For classical welding effectively use the plus on the electrode, and minus - on the terminal. At direct polarity of welding the minus on an electrode is provided, plus - on the "ground". The current moves from the electrode to the product. The electrode is cold, and the product is hot. This feature is widely used in special electrodes, which are designed for fast welding of stainless steel sheets.
The importance of polarity in welding
Naturally, that inverter AC welding does not depend, which is equipped with a transformer clamp to connect the product and the electrode. But DC is traditionally welded in several ways. Electrode, connected to the negative pole, with direct polarity is the cathode.
At the anode, connected to the positive pole, the product is transformed. Reverse polarity means, that the electrode after connection to the positive pole becomes the anode. The cathode in this position is a product, connected to the negative pole.
The material of the electrode sets the parameter of the arc between the non-melting electrodes of tungsten and fusible metal electrodes. Welding arc has a number of physical and technological properties. The result of the arc operation will depend almost entirely on this. Physical properties include:
- kinetic;
- electromagnetic and temperature;
- electric and light.
There are three main technological properties:
- arc power;
- spatial stability;
- self-regulation.
To support the combustion of the arc, you need to create reverse electrically charged parts in the space between the electrodes. These particles are electrons, as well as positive and negative ions. Their transformation is called ionization. Gas, having electrons and ions, which is called ionized.
The arc gap is ionized during arc ignition, and is constantly maintained during its combustion. In the interval of the arc, usually, highlight the following areas:
- arc discharge area;
- anodic;
- cathodic.
There is a significant voltage drop in the anode region, caused by the accumulation of charged electrodes of charged particles. Electrode spots begin to appear on the surface of the anode and cathode, which represent a kind of foundation of the arc column. Through them the route of current to welding is laid.
Welding has a total arc size, it consists of the total lengths of 3 areas. The total arc voltage is the sum of the voltage drops in each part of the arc. The dependence of the voltage on the size of the arc is the sum of the voltage drop in the near-cathode and near-anode sections. The specific voltage drop in the arc is one millimeter from the arc column. And the main characteristic of the arc is the heat output of the heating source.
Its efficiency is calculated taking into account the amount of heat, introduced into the metal per unit time. Thermal power is a part of the total arc thermal power, with which a certain proportion of heat is wasted unproductively:
- for heat dissipation in the product;
- radiation;
- to warm up the spray drops.
Arc welding technology

The advantage of arc welding is obvious. Welding differs in features:
- in the environment, where is the arc discharge;
- by type of current;
- by type of electrodes.
Semi-automatic arc welding in a protective gas environment is widely used to repair car bodies.. For private use, manual arc welding is the most affordable. It is made by fusible electrodes on alternating or direct current. This is a good chance to weld most of the metals in a non-factory environment.
The size between the surface of the main product and the bottom of the crater is the depth of penetration or penetration. Depth depends:
- values of welding current;
- from the speed of the arc.
If the size of the welding arc is not more, than the size of the electrode rod, then this arc is called normal or short. It guarantees excellent seam quality. Arc, which has a large length, considered long. A very large increase in the size of the arc leads to a deterioration in the quality of welding. The influence of the magnetic field creates a deviation of the arc from a given direction. This is called an electromagnetic blast.
The electrode during the process moves along and across the weld in the axial direction, to save the specified arc size. Accelerated movement of the electrode leads to the formation of a narrow, uneven and loose seam. At slow movement there is a danger of overheating of material.
Welds are shaped:
- branded;
- overlapping;
- butt;
- angular.
The length of the seams are divided into continuous and intermittent. According to the spatial location have the following varieties:
- vertical;
- ceiling;
- lower;
- horizontal.
Power sources: transformer for welding, rectifier, generator - at the external indicator have a relationship between the magnitude of the load current with the voltage at the output terminals. Volt-ampere arc is the ratio between the voltage in static mode and the arc current. External indicators of welding generators are considered to be falling.
The size and shape of the seam is also affected by the type of electric current and its polarity. That is, DC reverse polarity provides a much greater melting depth, than direct current with direct polarity, this is due to the different amounts of heat, appearing on the anode with the cathode. As the speed of the welding process increases, the depth and width of the weld seam decrease.




